2023-04-29 19:52:38
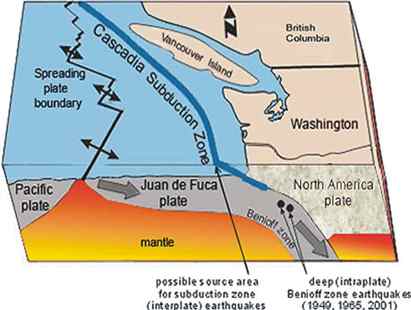
A study conducted by the University of Washington discovered a unique underwater hot spring approximately 80 kilometers off the coast of the state of Oregon, in the United States, in the fearsome Cascadia subduction zone, which forms the boundary between the tectonic plates of John of Fuca and North America.
From these points a warm fluid is released through four holes, a fact that could contribute to the prediction of earthquakes along the dangerous geological fault, which threatens to cause a megasissm and a powerful tsunami or tidal wave, capable of raising waves of about 30 meters, reports Live Science.
Scientists believe this fluid acts as a friction regulator in the fault zone, which could have catastrophic consequences for the Pacific Northwest if it ever disappears.
The Cascadia subduction zone, the marine fault line that stretches from Canada’s Vancouver Island to northern California.
The scientific report was published in Science Advances, and notes that off the coast of Newport, Oregon, on the seafloor 1,040 meters below the ocean’s surface, lie at least four small conduits bubbling fluids from deep within the fault. The authors named this underwater spring the ‘Oasis of Pythia’, after the priestess in Greek mythology who claimed to discover hidden things with the help of mind-altering gases from hot springs.
According to the study, the spring would come from water located about four kilometers below the seabed at the plate boundary, which regulates the stress on the offshore fault.
Each of the vents is about two inches in diameter, and they originate about four kilometers deep, near where the plates meet.
The escape of fluids through these slip faults is important because it reduces the fluid pressure between the sediment particles and therefore increases the friction between the oceanic and continental plates.
“If the fluid pressure is high, it’s like the air is on, which means there’s less friction and the two plates can slide. If the fluid pressure is lower, the two plates will lock; that’s when stress can build up,” explained Evan Solomon, one of the study’s authors.
Related article
Video: what the tsunami will be like after the dreaded earthquake in Cascadia, USA.
#Hot #Spring #Cascadia #Undersea #Fault