2024-12-17 19:40:00
Changes in the color of the earwax can indicate age, but also possible infections or the presence of foreign bodies in the ear.
Last update: December 17, 2024
The color of earwax, also called cerumen, is a telltale sign of its condition and function. From the characteristic pale yellow, through orange, brown and even black, Each variation reflects the passage of time or situations related to our hearing health.
Newly produced wax is soft and light in color, while older wax dries out and darkens. This transformation corresponds to a natural defense mechanism, which protects the ear from the entry of dust, dirt or bacteria.
However, sometimes, Clogging due to excessive buildup, infection and disease also causes changes in color and consistency. which do not go unnoticed. If you notice an unusual tone right now that worries you, find out what it means and when to see a doctor.
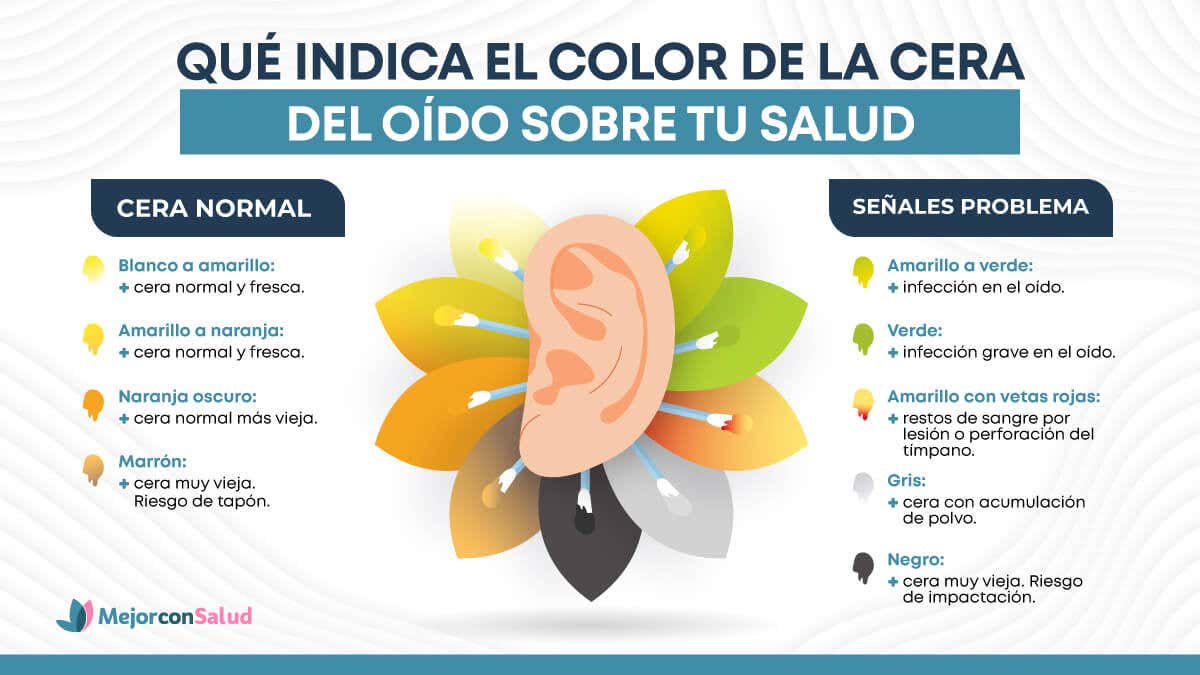
There are wax colors that are considered normal, while others may pose a problem.
1. White to yellow
When the ear is healthy and earwax production is normal, its color can vary from whitish to golden yellow. It is often accompanied by a soft, sticky and moist consistency, which is what allows it to perform its protective function to prevent the entry of infectious particles or microorganisms.
It is also an indication that the ear’s ceruminous glands are functioning optimally and that there is no interference in the debris removal process. This happens naturally with movements when speaking or chewing.
2. Yellow to orange
That the color of earwax varies between yellow and orange tones is completely normal and does not indicate health problems. The main reason these changes occur has to do with the oxidation of the wax, a process that occurs over the course of days as the substance mixes with dead cells and other particles.
The amount of earwax produced, as well as the ear’s contact with shampoos, conditioners and other products, influence whether it is more or less dark. Another hypothesis suggests that consuming certain foods (such as those containing fats, sugars, and strong pigments) affects the appearance of wax, but there is no evidence to prove this.
3. Dark orange
As the days go by, and if the removal of the wax has any kind of interference, its color may turn to dark orange. Additionally, its texture becomes more sticky or crumbly, which increases the risk of blockages or plugs in the ear canal.
To avoid this, you can clean the ear with special drops, such as those containing hydrogen peroxide, acetic acid or sodium bicarbonate. They are usually sold over the counter in pharmacies and their use is simple:
- Place 5 drops in each ear (or as indicated on the product), tilt your head to the opposite side for a few minutes and finally turn your head to drain any residue. You can clean the outside with a soft, clean cloth.
4. Brown
A variation between dark orange and brown in earwax suggests that the residue has been accumulated for a long time and has aged. Its consistency is much thicker, a product of mixing with dust particles, dead cells and secretions.
Since its consistency is thicker and stickier, it tends to stick. Over the course of days, the blockage will cause itching, decreased hearing, and an increased risk of infections. This is why it is essential to contact the specialist, the otolaryngologist, to carry out a safe and effective cleaning.
5. Yellow to green
Earwax that changes color from yellow to green indicates the presence of an ear infection. In these circumstances, pus or secretions caused by bacteria explain the alteration. Symptoms such as pain, itching and fever can occur at the same time.
Depending on the severity of the condition, earwax may also feel thinner, thicker, or stickier. It may also smell bad. To avoid complications, it is essential to seek medical help as soon as possible. The specialist can prescribe antibiotic drops.
6.Green
A serious ear infection that is not treated in time can cause the wax to turn from pale to dark green. This type of discharge is usually sticky, so it tends to cause blockage of the ear canal. Furthermore, it is smelly and occurs along with pain, irritation, fever, hearing loss and dizziness.
After performing diagnostic tests to determine the type of infection, your ear, nose and throat doctor may prescribe antibiotic ear drops and oral antibiotics. Treatment should be completed as indicated, even if symptoms improve.
If you see no improvement after 48 to 72 hours, you may need to try a different antibiotic.
When treatment is unsuccessful or the infection recurs over periods of 6 to 12 months, your doctor may order placement of tympanostomy tubessurgery in which a small tube is inserted into the eardrum to facilitate the passage of air and the drainage of liquids.
7. Yellow with red veins
Noticing red streaks in yellow wax suggests the presence of blood, and there are several possible causes. In most cases it occurs due to scratches, wounds or insect bites.which are usually not serious and improve on their own within a few days.
You should avoid pinching or scratching your ear to avoid complications.
Tympanic perforation, however, is another cause of the alteration. Its appearance occurs due to serious infections, changes in blood pressure, loud noises or trauma. In addition to bleeding, symptoms include severe pain, hearing loss, a feeling of pressure in the ear, ringing and dizziness.
Mild cases improve with self-care, such as using warm compresses and taking over-the-counter pain relievers to relieve pain. It is recommended to keep your ear clean and dry, as well as avoid swimming or putting your head under water.
If the rupture of the eardrum is considerable or does not heal on its own, there are other interventions that can be used: tympanoplasty, which consists of repairing the affected area with the patient’s own tissues; and myringoplasty, which uses a special gel or paper to fix the perforations. Both options are performed in the office under anesthesia.
8. Grey
Gray earwax is usually the result of the accumulation of dust and environmental particles. In most cases it is harmless, but sometimes it is difficult to remove as it becomes dry and thick.
To avoid this, simply clean carefully and apply special drops or saline solution. If there are signs of obstruction, such as decreased hearing, it is best to see your doctor so he can perform flushing or suctioning.
9. Negro
Wax that remains in the ear canal for a long time oxidizes, hardens and acquires a black color. Since it is difficult to remove through the ear’s natural cleaning mechanism, it generates an occlusion, that is, a partial or total obstruction, which causes pain, decreased hearing and a greater risk of infections.
It is necessary for the doctor to intervene with otic irrigation or ear aspiration. These procedures are painless, but require extreme care to avoid inflammation or trauma.
Earwax is a substance you shouldn’t ignore
It is necessary to remember that, contrary to popular belief, earwax It is not a waste substance nor a sign of poor hygiene. Its adequate production is what allows us to lubricate, clean and protect the ear canal from bacteria and fungi.
At the same time, changes in color, texture or odor serve as a clue that something is wrong or that hygiene habits need to be strengthened. So instead of overlooking the changes, specify whether they are unusual and require medical intervention.
Prompt care can prevent infections, trauma or changes in ear function from generating serious complications or loss of quality of life.
#color #earwax #health

