Breakthrough drug NU-9 Halts Early Alzheimer’s Development in Animal Trials
Table of Contents
A novel treatment, NU-9, has demonstrated the ability to halt the early progression of Alzheimer’s disease in an animal model, offering a potential new avenue for preventative therapies. The groundbreaking research, slated for publication on December 18 in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia, identifies a specific toxic trigger of the disease and suggests intervention before the onset of symptoms could be key to success.
Targeting the Root of Alzheimer’s: A New Beta-Amyloid Subtype
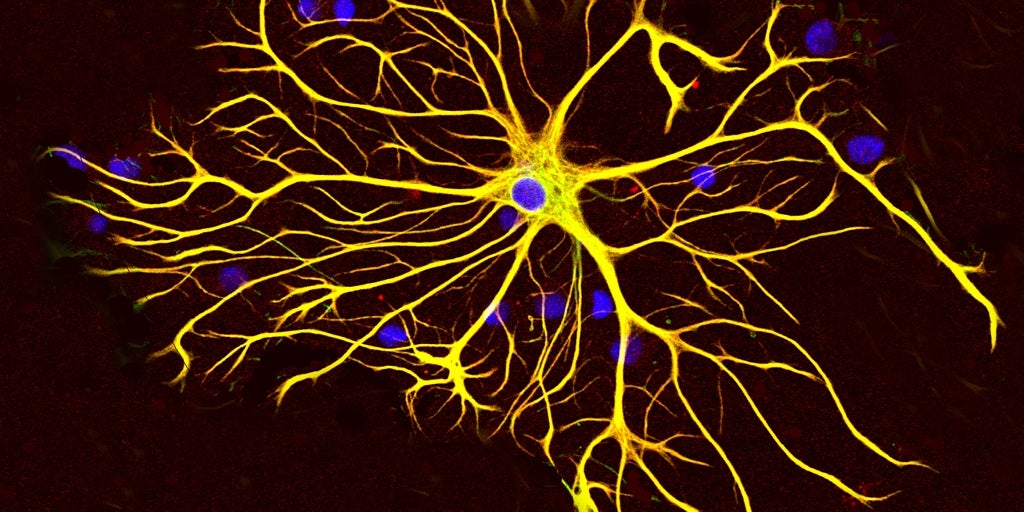
Scientists from the University of Northwestern (USA) have pinpointed a previously unknown and highly toxic subtype of beta-amyloid oligomers – small,misfolded protein clumps – as a primary instigator of early brain changes associated with Alzheimer’s.These changes manifest as neuronal dysfunction, inflammation, and the abnormal activation of immune cells within the brain.
The study revealed that NU-9 considerably reduces the presence of this particularly damaging subtype, mitigating the resulting inflammation and other critical disease markers in mice. researchers observed that the drug specifically lessened the abnormal activation of astrocytes – cells normally responsible for protecting neurons, but which can become detrimental in Alzheimer’s – and decreased levels of an altered form of the protein TDP-43, linked to cognitive decline.
The Promise of Preventative Treatment
“Alzheimer’s disease begins decades before symptoms appear,” explains a led researcher.”When it is diagnosed, the brain damage is already very advanced. That is why many clinical trials have failed: they start too late.” This finding underscores the critical importance of early intervention,shifting the focus from treating symptoms to preventing the disease’s onset.
NU-9’s potential as a preventative measure is particularly compelling. researchers suggest it could function similarly to medications used to manage cholesterol and prevent heart disease – intervening before irreversible damage occurs.
From ALS to Alzheimer’s: A Versatile Drug Candidate
interestingly, NU-9 was initially developed as a treatment for other neurodegenerative diseases, and has already shown promise in animal models of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). in 2024, the drug received regulatory approval to begin human clinical trials for ALS, paving the way for potential broader applications.
Identifying ACU193+: A key Discovery
The moast notable finding of the new study centers on the identification of a specific beta-amyloid subtype, designated ACU193+. This subtype appears very early within neurons and afterward accumulates in nearby astrocytes, triggering an inflam
Here’s a substantive news report based on the provided text, answering the “Why, who, What, and How” questions:
New Drug NU-9 Shows Promise in Halting Early Alzheimer’s Development
Evanston, IL – A new drug, NU-9, has demonstrated the ability to halt the early progression of Alzheimer’s disease in animal trials, offering a potential preventative therapy. The research, published December 18 in Alzheimer’s & Dementia, identifies a specific toxic trigger of the disease and suggests early intervention is key.
What happened? Scientists at the University of Northwestern (USA) discovered a highly toxic subtype of beta-amyloid oligomers, designated ACU193+, which appears to be a primary instigator of early brain changes associated with Alzheimer’s. NU-9 significantly reduced the presence of this subtype in mice,mitigating inflammation and other disease markers.
Who is involved? Researchers at the university of Northwestern led the study.The drug, NU-9, was