Invisible Ink & Advanced Imaging: Researchers Unveil Future of Document Interaction & Biometrics
Researchers have developed groundbreaking technologies capable of embedding digital information invisibly within printed materials and enhancing medical imaging with portable, AI-powered devices. These innovations, presented at the 2025 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems in Yokohama, Japan, promise to revolutionize how we interact with the physical world and advance healthcare diagnostics.
The Dawn of “Imprinta”: Digital Information Hidden in Plain Sight
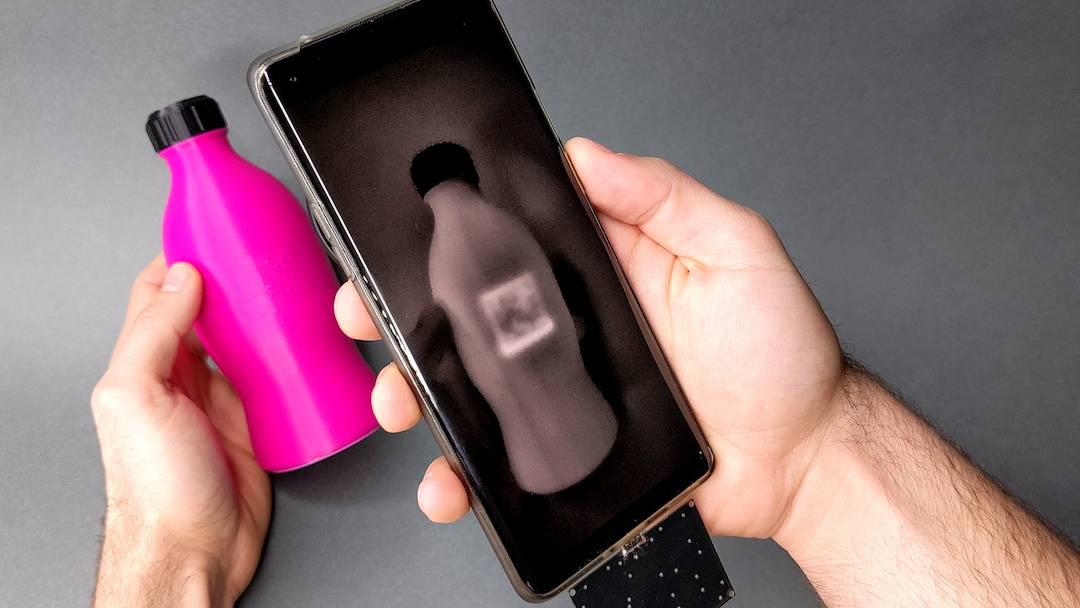
A team from the Carlos III University of Madrid (UC3M) and the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has created Imprinta, a system that utilizes infrared ink to embed digital information within printed documents. This information remains invisible to the naked eye but is detectable by a specialized infrared camera. The goal is to enable advanced interaction with physical documents without altering their visual appearance.
“Imprinto uses an invisible infrared ink to the human eye, but detectable by a nearby infrared sensitive chamber, such as the one that can be integrated into mobile devices through a simple modification of the photographic sensor,” explained a lead researcher from the UC3M’s Department of Electronic Technology. This technique has far-reaching implications, opening doors to improved product traceability, secure document authentication, and enriched educational and professional content. Crucially, the system operates without relying on visible codes like QR codes or requiring additional hardware attached to the document.
Beyond Documents: Expanding Applications with “Bright Marker”
The UC3M team’s innovations extend beyond traditional documents. Bright Marker is a system designed to embed invisible codes within 3D objects using fluorescent polymers. This allows for the creation of objects containing hidden digital labels, offering benefits for industrial traceability, streamlined logistics, and personalized experiences within augmented reality environments – all without compromising the object’s aesthetic.
Revolutionizing Medical Diagnostics with “Vibes”
In a parallel development, the researchers have also unveiled Vibes, a portable camera connectable via USB-C to any mobile device. This device allows for the visualization of veins beneath the skin, aiding in more effective medical interventions. Furthermore, Vibes utilizes artificial intelligence algorithms to perform biometric recognition based on the unique vascular patterns of the palm.
“The system intends to study in real time the images captured, allowing not only the visualization in 2D but also the 3D reconstruction of the venous depth by techniques such as stereoscopy or Time-of-Flight,” a researcher added. This capability could significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of various medical procedures.
A Vision for Augmented Reality Integration
These advancements are not isolated projects but rather components of a larger vision. Researchers envision a future where augmented reality glasses or similar wearable technology replace traditional mobile phones. These devices, equipped with integrated infrared chambers, would be capable of recognizing and interpreting the environment, seamlessly blending the digital and physical worlds. This future hinges on the ability to unobtrusively embed and interpret digital information within our surroundings, a challenge these new technologies are poised to address.