Prokaryotic cells are the cells that make up bacteria, those microorganisms that coexist with us for good (hello, good microbiota of the intestine, skin…) but also for bad (goodbye, pathogenic bacteria that cause us diseases).
are cells a lot simpler than eukaryotic cells (whether they are animals or plants) but that simplicity does not mean that they are less important. possibly thanks to that replicate and evolve rapidly colonizing In a short time, places where conditions are favorable, and if they are not, they have many ways to mutate and adapt (for this reason, we are increasingly finding bacteria resistant to antibiotics and superbugs, a serious problem).
Without further delay, we are going to see the main characteristics of the prokaryotic cell.
They don’t have a nucleus, they have a nucleoid.
Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus where the DNA is protected, but the DNA is in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. This is the main characteristic of prokaryotic cells and the one that makes it easier to identify them.
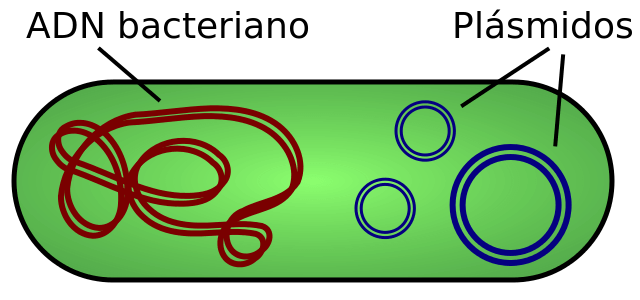
DNA forms a single chromosome
The DNA forms a single bacterial chromosome that is formed by a circular DNA double helix where all the information for the functioning of the cell is found. It is associated with non-histone proteins (unlike the eukaryotic cell).
plasmids
Bacteria can have inside, in addition to their DNA, small rings of DNA independent of the chromosome called plasmids. These plasmids are very important because they are related to the ability of bacteria to exchange genetic material, and they are also responsible for resistance to antibiotics that we have discussed before.
There are two main types of plasmids:
- Fertility or F factor plasmids: are those that allow genetic exchange in bacteria by conjugation.
- R plasmids (resistance plasmids): are the plasmids in which the genes responsible for resistance to antibiotics that are passed from mothers to daughters are usually found. It can also be transferred to the bacterial chromosome, or passed to viruses or bacteria. An R plasmid can carry genes encoding resistance to one or more antibiotics.
- There are other types of plasmids that provide the ability to generate toxins, to degrade certain compounds, to give certain metabolic capacities…
When a person takes many antibiotics, the bacteria with R plasmids end up being selected, that is, those that are increasingly resistant to antibiotics, which can cause serious health problems.
They have a cell wall and a plasma membrane.
Prokaryotic cells have a plasma membrane and a cell wall that is different from that of the plant cell. It is composed of murein (a peptidoglycan) and is found on the outside of the plasma membrane.
The bacterial cell wall can be of two types, which leads to classifying bacteria into two types:
- Gram +: are bacteria that stain by Gram stain. They have a single thick basal layer composed of murein.
- Gram -: are bacteria that do not stain by Gram stain. They have a double layer composed of a thin basal layer of murein on which there is a double lipid layer called the outer membrane.
Gram stain is a special staining method to differentiate the structure of bacteria devised by Hans Christian Gram in 1884.
may have capsule
Another characteristic of prokaryotic cells is that some bacteria can have a capsule. It is composed of polymers and is outside the cell wall. Its function is protective (from phagocytosis, from desiccation) but it also has other functions such as being the place of deposit of waste substances or allowing their adhesion.
Its cytoskeleton is simple.
Although at first it was thought that bacteria did not have a cytoskeleton such as that of eukaryotic cells that allows the mobility of organelles within the cell, they do have three proteins that are responsible for giving structure to the cell.
have ribosomes
This is important since ribosomes are responsible for manufacturing (synthesizing) proteins from RNA. They have two parts (subunits) and their size is smaller than that found in eukaryotic cells.
they have no organelles
Bacteria do not have organelles that allow them to carry out complex functions such as chloroplasts, mitochondria or the Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum… but this does not prevent them from being able to colonize almost all existing environments on planet Earth.
They may have cilia and flagella
Although its structure is different from the eukaryotic cell, bacteria can have flagella that help them move and propel themselves.
Small size
The size of the prokaryotic cell is small but without reaching the size of the virus. They are comparatively between eukaryotic cells and viruses.
They do not form multicellular organisms
Prokaryotic cells are not capable of forming multicellular organisms such as an animal or a plant, but are unicellular organisms that can live in colonies but can live independently.
