The global device-as-a-service (DaaS) market is projected to surge from $83 billion in 2022 to a staggering $757 billion by 2030, signaling a massive shift in how businesses acquire and manage technology. This model transforms PCs, smartphones, and other mobile computing devices into a paid service, essentially outsourcing hardware, software, and device management to external providers.
A subscription-based approach to technology, Device as a Service is reshaping business IT procurement.
- Device as a Service (DaaS) offers PCs and mobile devices on a subscription basis.
- The global DaaS market is expected to grow to $757 billion by 2030.
- DaaS simplifies IT by handling hardware, software, and device management.
- Key benefits include cost predictability and reduced IT workload for businesses.
- Potential drawbacks involve lack of ownership and potential privacy concerns.
Shifting Costs from Capital to Operating Expenses
Table of Contents
Think of it like leasing a car instead of buying one. You get the latest model, maintenance is frequently enough included, and you can upgrade when the lease is up.For businesses,this means ditching the huge upfront costs,known as capital expenditures (CAPEX),for predictable operating expenses (OPEX). This is particularly attractive for smaller startup organizations looking to scale their tech without breaking the bank.
The trend toward “anything as a service” (XaaS) has gained serious traction. Back in 2014,only one percent of PCs shipped as part of a DaaS program. Fast forward to today, and the market is exploding.
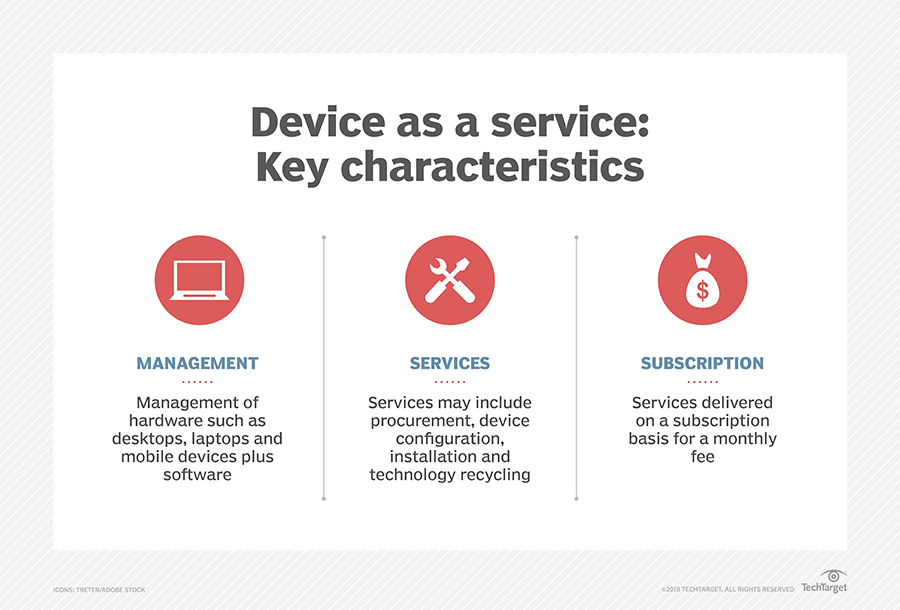
How Device as a Service Works
Under a DaaS contract, providers typically cover hardware like PCs, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. They also manage the software,including pre-installation and updates. Services often extend to device backups,asset tracking,security measures,and responsible end-of-life disposal.Payment is usually on a per-device basis, wiht contracts often stipulating two, three, or five-year timelines for device upgrades.
What makes up DaaS?
The model is built on three core pillars:
- Device fulfillment: Providers supply businesses with up-to-date, preconfigured technology, bypassing large upfront purchases.
- Device services: This encompasses ongoing support, maintenance, security patches, and essential IT management to keep devices running smoothly.
- Device recovery: Securely handling the collection, refurbishment, or disposal of old devices, while ensuring sensitive data is protected.
Who is Using Device as a Service?
DaaS is gaining traction across a wide range of industries, including:
- Retailers (both online and brick-and-mortar)
- Educational institutions
- Financial service providers
- Government agencies
DaaS vs. Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
It’s easy to confuse “device as a service” with “desktop as a service” because they share the DaaS acronym.The key difference? Device as a service provides actual physical hardware-like laptops and smartphones-on a subscription. Desktop as a service,conversely,is a cloud-based offering where you access a virtual desktop running on a remote server. While desktop-as-a-service providers typically bill monthly per virtual desktop, device-as-a-service agreements usually involve annual or multiyear commitments.

