2024-04-09 03:04:14
A recent discovery reveals an immense volcano in Marte, located near the equator, along with signs of ice nearby. Announced in the 55th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, the discovery transforms what was previously known about the Red Planet and points to new potential areas for life and key resources for future exploration. Provisionally referred to as “Mars and that could be active”>Noctis volcano«, this volcanic colossus and the possible ice capwhich had been hidden by erosion, open new scientific and exploratory frontiers on the red planet.
The Noctis volcano, located in one of the most emblematic and geologically rich areas of Mars, stands out not only for its size, with an impressive height and extension, but also for its complex geological history. The possible presence of ice near its base adds greater interest to the scientific community, since it suggests that Mars may harbor vital resources more accessible than previously thought.
The giant volcano is among the largest volcanic provinces and canyons on Mars. Photo: NASA/Lee and Shubham
The discovery, made by a team led by Dr. Pascal Lee from high school SETI and the Marte Institute, was based on the detailed analysis of images and data collected by the NASA of several missions to Mars, which has shown how the planet still keeps secrets despite decades of exploration
“We were examining the geology of an area where we had found the remains of a glacier last year when we realized that we were inside a huge, deeply eroded volcano,” said lead author Pascal Lee, an astronomer at the SETI Institute. and the Marte Institute, in an official statement.
What is the volcano discovered on Mars like?
The Noctis volcano has a height greater than 9000 meters and an extension of approximately 450 kilometers. Regarding its appearance, the team of experts has indicated that it does not present the conventional cone shape that volcanoes usually have because a long history of deep fracturing and erosion has modified it.
Located in the eastern part of the volcanic province Tharsisthe presence of Noctis is considered irrefutable proof of the active geological processes that have shaped the planet’s surface over millennia.
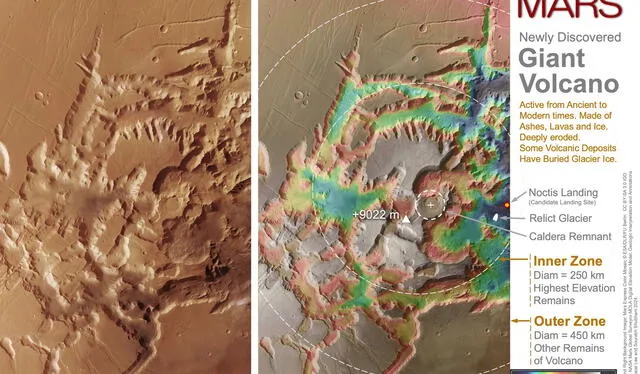
Images from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) were used. Photo: NASA/Lee and Shubham
“Near the center of the structure you can see a caldera remnant, the remains of a collapsed volcanic crater that once housed a lava lake. In several areas within the perimeter of the volcanic structure, lava flowspyroclastic deposits and deposits hydrothermal minerals«, indicate notes by Lee and Sourabh Shubham, co-authors of the research.

