Cloud-9: Astronomers Discover a “Failed galaxy” Offering Clues to Early Universe Formation
Table of Contents
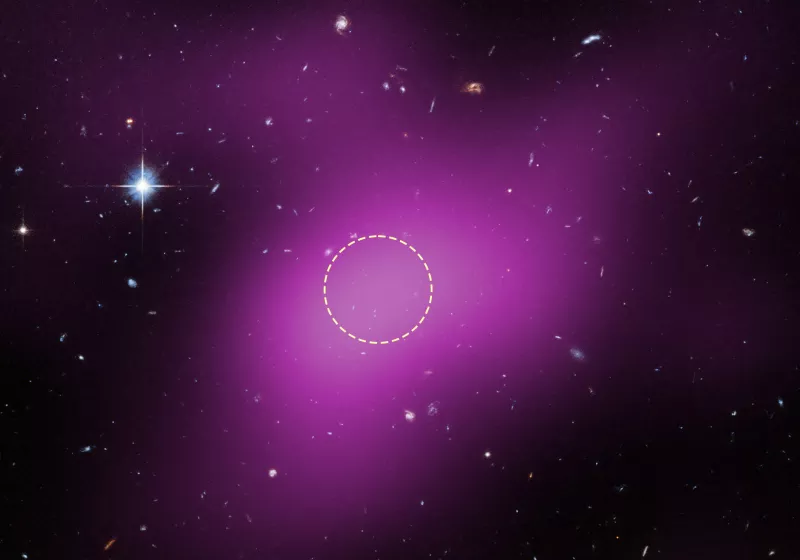
A newly studied cosmic structure, dubbed Cloud-9, is challenging conventional understanding of galaxy formation, with researchers identifying it as a potential “failed galaxy” – a remnant from the universe’s earliest stages. This discovery provides a unique window into the building blocks of galaxies and the processes that shaped the cosmos.
Astronomers are increasingly focused on understanding the origins of galaxies,and Cloud-9 presents a rare opportunity to examine a system that never fully coalesced. The structure, described as a “relic” of early galactic progress, offers insights into the conditions present in the nascent universe.
Unveiling the Remnants of a Proto-Galaxy
The research suggests that Cloud-9 represents a basic building block of a galaxy that ultimately did not achieve full formation. This means it contains the raw materials – gas and dust – that would have been necessary to create a fully-fledged galaxy, but lacked the conditions to trigger complete star formation.
According to Alejandro Benitez-Llambay, the cloud can be considered a crucial component in understanding how galaxies initially began to assemble. This perspective shifts the focus from fully formed galaxies to the smaller, less-developed structures that preceded them.
Implications for Early Universe Models
The existence of structures like Cloud-9 supports the idea that the early universe was filled with numerous smaller clumps of matter. These clumps, through gravitational interactions, eventually merged to form the larger galaxies we observe today. However, not all of these clumps succeeded in becoming galaxies.
This discovery has significant implications for cosmological models.It suggests that the process of galaxy formation was not always successful, and that many potential galaxies may have remained in a fragmented, undeveloped state.Further study of Cloud-9 and similar structures could refine our understanding of the factors that determine whether a proto-galaxy thrives or fails.
A Unique Opportunity for Astronomical Study
Cloud-9’s unique status as a “failed galaxy” makes it an invaluable object for astronomical study. By analyzing its composition and structure, scientists can gain a better understanding of the conditions that were prevalent in the early universe. This knowledge can then be used to improve our models of galaxy formation and evolution.
The study of Cloud-9 underscores the complexity of the universe and the ongoing quest to unravel its mysteries. It highlights the importance of examining not only the successes of galaxy formation, but also the failures, to gain a complete picture of cosmic evolution.
Why: Astronomers are seeking to understand how galaxies formed in the early universe. The discovery of Cloud-9, a “failed galaxy,” provides a unique opportunity to study a structure that never fully developed into a galaxy, offering insights into the conditions and processes of early galaxy formation.
Who: The research was led by Alejandro Benitez-Llambay and a team of astronomers. The article doesn’t specify the full team or their affiliations.
What: Astronomers have discovered Cloud-9, a cosmic structure identified as a “failed galaxy.” It’s a remnant of the early universe containing the raw materials for galaxy formation (gas and dust) but lacking the conditions for complete star formation.
How did it end?: The study of Cloud-9 is ongoing. Currently, scientists are analyzing its composition and structure to refine models of galaxy formation. The discovery doesn’t have a definitive “end” but represents a continuing line of inquiry into the early universe and the processes that shaped it.