“`html
Jupiter’s dazzling Auroras: A New Perspective from the James webb Space Telescope
Table of Contents
- Jupiter’s dazzling Auroras: A New Perspective from the James webb Space Telescope
- Unveiling the Unexpected: JWST’s Christmas Day Finding
- the Power of Collaboration: JWST and Hubble Team Up
- Why Study Jupiter’s Auroras? Unlocking the Secrets of Space Weather
- The Mystery deepens: Unexplained Brightness and Future Research
- Future Developments: What’s Next for Jupiter Research?
- The Broader Implications: Understanding Planetary Magnetospheres
- FAQ: Your Questions About jupiter’s Auroras Answered
- Pros and Cons: The benefits and Challenges of Studying Jupiter’s Auroras
- Jupiter’s dazzling Auroras: A New Perspective from the James webb Space Telescope
- Unveiling the Unexpected: JWST’s Christmas Day Finding
- the Power of collaboration: JWST and Hubble Team Up
- Why Study Jupiter’s Auroras? Unlocking the Secrets of Space Weather
- The Mystery deepens: Unexplained Brightness and Future Research
- Future Developments: What’s Next for Jupiter Research?
- The Broader implications: Understanding Planetary Magnetospheres
- FAQ: yoru Questions About jupiter’s Auroras Answered
- Pros and cons: The benefits and Challenges of Studying Jupiter’s Auroras
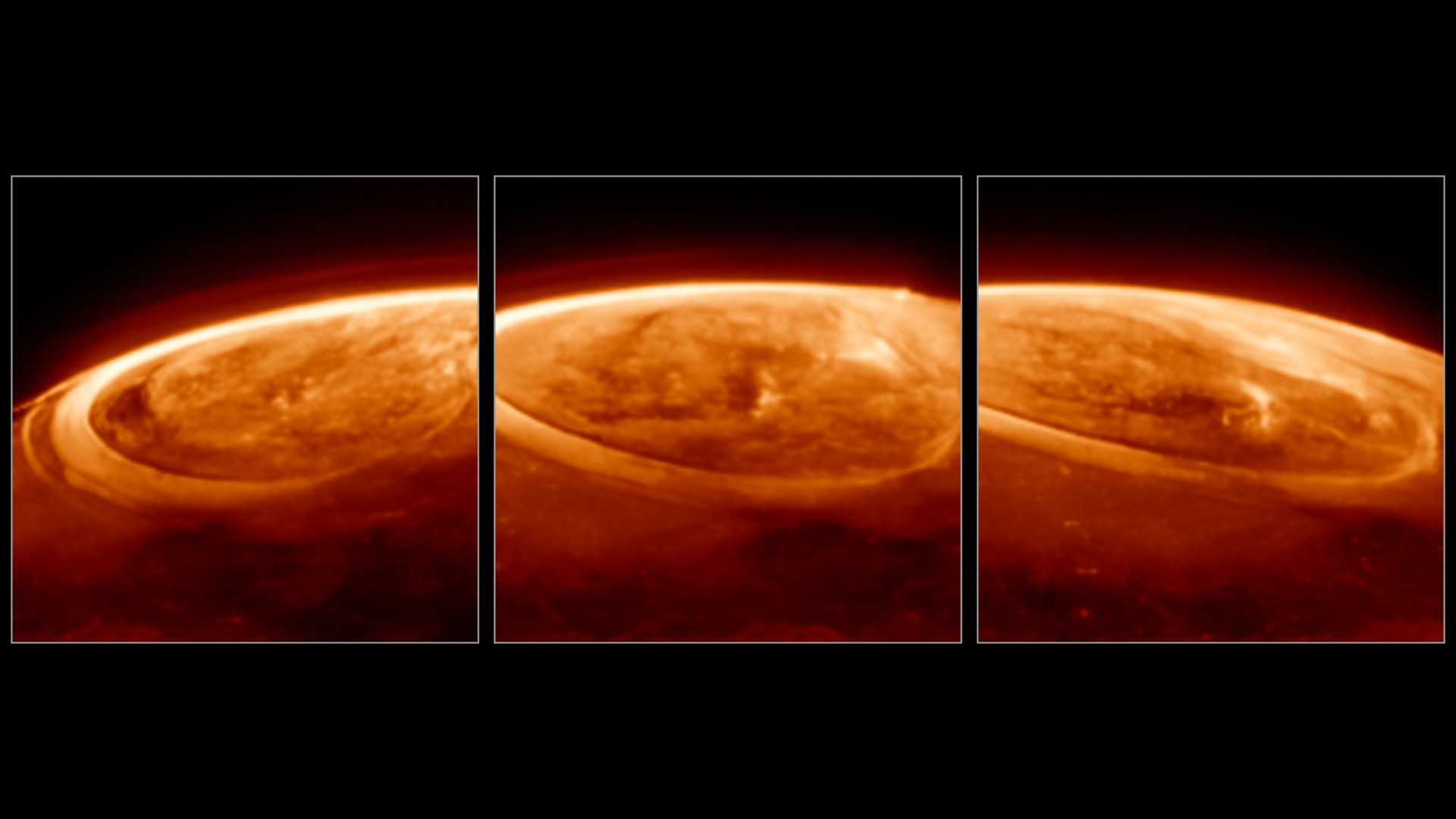
Imagine unwrapping a Christmas present so remarkable it redefines what you thought you knew about the universe. That’s precisely what happened when the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) turned its gaze towards Jupiter on December 25, 2023, capturing auroras unlike anything seen before.
These weren’t just pretty lights; they were dynamic, intense displays that left scientists “scratching thier heads” and rewriting the textbooks on planetary auroras. What secrets do these celestial light shows hold, and what can they tell us about the forces shaping our solar system?
Unveiling the Unexpected: JWST’s Christmas Day Finding
Jonathan Nichols, a planetary aurora specialist at the University of Leicester, described the experience as being “blown away.” The initial expectation was to observe auroras that faded in and out gradually, perhaps over fifteen minutes or so. Instead, the entire auroral region was “fizzing and popping with light,” changing sometimes within seconds.
This rapid variability was a complete surprise, challenging existing models of how Jupiter’s auroras behave.It’s like expecting a slow, gentle snowfall and instead witnessing a blizzard of light.
the Power of Collaboration: JWST and Hubble Team Up
The JWST’s observations were further enhanced by simultaneous data collected by the Hubble Space Telescope. By combining the infrared capabilities of JWST’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) with Hubble’s ultraviolet sensors, scientists gained a more complete picture of Jupiter’s auroras.
However, this collaboration also revealed a perplexing mystery: some of the brightest light observed by JWST had no corresponding feature in Hubble’s images. This discrepancy has sparked intense debate and further examination into the underlying mechanisms driving these auroras.
The Infrared Advantage: Seeing the Unseen
JWST’s ability to observe in the infrared spectrum is crucial for studying jupiter’s auroras.Infrared light can penetrate the planet’s hazy atmosphere, revealing details that are invisible to telescopes operating in visible or ultraviolet light. This allows scientists to study the composition, temperature, and dynamics of the auroral regions with unprecedented precision.
think of it like using night-vision goggles to see in the dark. JWST’s infrared vision allows us to see the hidden features of Jupiter’s auroras, revealing a world of complexity and dynamism.
Why Study Jupiter’s Auroras? Unlocking the Secrets of Space Weather
Understanding Jupiter’s auroras is not just about admiring pretty lights. These auroras are a direct result of the interaction between Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field and the solar wind, a stream of charged particles constantly emitted by the Sun.
By studying these interactions, scientists can gain valuable insights into the fundamental processes that govern space weather, which can have notable impacts on earth, affecting everything from satellite communications to power grids.
Space Weather and Earth: A Critical Connection
Severe space weather events, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can disrupt our technological infrastructure and even pose risks to astronauts in space. Understanding how these events interact with planetary magnetic fields is crucial for developing better forecasting models and mitigation strategies.
Jupiter, with its immense magnetic field, serves as a natural laboratory for studying these interactions on a grand scale. By learning how Jupiter’s magnetic field responds to the solar wind, we can better understand and prepare for similar events that could impact Earth.
The Mystery deepens: Unexplained Brightness and Future Research
The fact that JWST observed shining auroral features that were not visible to Hubble raises fundamental questions about the processes driving these light shows. What is causing this discrepancy, and what does it tell us about the composition and dynamics of Jupiter’s atmosphere?
Scientists are now exploring several possible explanations, including variations in the energy and composition of the particles precipitating into Jupiter’s atmosphere, and also differences in the sensitivity of the two telescopes to different wavelengths of light.
Possible Explanations: A Scientific Detective Story
One hypothesis is that the bright features observed by JWST are caused by high-energy particles that emit primarily in the infrared spectrum.These particles might potentially be accelerated by specific processes within Jupiter’s magnetosphere, leading to localized regions of intense infrared emission.
Another possibility is that the composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere varies significantly in the auroral regions, leading to differences in the way it interacts with the incoming particles. further research is needed to determine the precise cause of the observed discrepancies.
Future Developments: What’s Next for Jupiter Research?
The JWST’s observations of Jupiter’s auroras are just the beginning.These initial findings have opened up a new window into the dynamics of this giant planet, and future research promises to reveal even more secrets.
Scientists are planning to use JWST to conduct further observations of Jupiter’s auroras,focusing on different wavelengths of light and different regions of the planet. they also hope to coordinate these observations with other telescopes, both on Earth and in space, to obtain a more thorough picture of the auroral phenomena.
The Juno Mission: A Complementary Perspective
NASA’s Juno spacecraft,which is currently orbiting Jupiter,provides a complementary perspective on the planet’s auroras. Juno is equipped with instruments that can measure the magnetic fields and charged particles in jupiter’s magnetosphere,providing valuable context for interpreting the JWST observations.
By combining the data from JWST and Juno, scientists can gain a more complete understanding of the complex interactions between Jupiter’s magnetic field, atmosphere, and the solar wind.
The Broader Implications: Understanding Planetary Magnetospheres
The study of Jupiter’s auroras has broader implications for our understanding of planetary magnetospheres in general. Magnetospheres are the regions of space surrounding planets that are dominated by their magnetic fields. These regions protect planets from the harmful effects of the solar wind and play a crucial role in shaping their atmospheres.
By studying the magnetospheres of different planets, including Jupiter, Earth, and even exoplanets orbiting other stars, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental processes that govern the evolution and habitability of planetary systems.
Exoplanet Auroras: A Search for Habitable Worlds
The detection of auroras on exoplanets could be a key indicator of their habitability. Auroras are a sign that a planet has a magnetic field,which can protect its atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind. A stable atmosphere is essential for maintaining liquid water on the surface, which is considered a prerequisite for life as we know it.
Future telescopes, such as the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) currently under construction in Chile, may be able to detect auroras on exoplanets, providing valuable clues about their potential to harbor life.
FAQ: Your Questions About jupiter’s Auroras Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about Jupiter’s auroras, based on the latest research and expert insights:
What causes auroras on Jupiter?
auroras on Jupiter are caused by the interaction between the planet’s powerful magnetic field and charged particles from the solar wind and Jupiter’s own moons, particularly Io. These particles are accelerated along Jupiter’s magnetic field lines and collide with atoms and molecules in the planet’s atmosphere, causing them to emit light.
How are Jupiter’s auroras different from Earth’s auroras?
Jupiter’s auroras are much more powerful and dynamic than Earth’s auroras. They are also influenced by different factors, such as the planet’s rapid rotation and the presence of volcanic moons like Io. Additionally, Jupiter’s auroras emit light across a wider range of the electromagnetic spectrum, including infrared, which is not typically seen in Earth’s auroras.
Why are scientists so interested in studying Jupiter’s auroras?
Studying Jupiter’s auroras provides valuable insights into the fundamental processes that govern space weather and planetary magnetospheres. By understanding how Jupiter’s magnetic field interacts with the solar wind, scientists can better predict and prepare for similar events that could impact Earth. Additionally, the study of Jupiter’s auroras can definitely help us understand the potential habitability of exoplanets.
What role does the James Webb Space Telescope play in studying Jupiter’s auroras?
The James Webb Space Telescope’s infrared capabilities allow scientists to study Jupiter’s auroras in unprecedented detail. Infrared light can penetrate Jupiter’s hazy atmosphere, revealing features that are invisible to telescopes operating in visible or ultraviolet light. This allows scientists to study the composition, temperature, and dynamics of the auroral regions with greater precision.
What are some of the mysteries surrounding Jupiter’s auroras?
One of the biggest mysteries surrounding Jupiter’s auroras is the discrepancy between the observations made by JWST and Hubble. JWST observed bright auroral features that were not visible to Hubble, raising questions about the processes driving these light shows. Scientists are also working to understand the rapid variability of Jupiter’s auroras and the role of Jupiter’s moons in shaping their behavior.
Pros and Cons: The benefits and Challenges of Studying Jupiter’s Auroras
Like any scientific endeavor, the study of Jupiter’s auroras has both its benefits and challenges:
Pros:
- Improved understanding of space weather: Studying Jupiter’s auroras can help us better understand and predict space weather events that could impact Earth.
- Insights into planetary magnetospheres: Jupiter’s magnetosphere serves as a natural laboratory for studying the fundamental processes that govern these regions.
- Potential for exoplanet discovery: The detection of auroras on exoplanets could be a key indicator of their habitability.
- Advancement of telescope technology: the study of Jupiter’s auroras pushes the limits of telescope technology, leading to new innovations and discoveries.
Cons:
- Distance and accessibility: jupiter is a long way away, making it tough and expensive to send spacecraft and telescopes to study it.
- Complex data analysis: The data collected from Jupiter’s auroras
Jupiter’s dazzling Auroras: A New Perspective from the James webb Space Telescope
imagine unwrapping a christmas present so remarkable it redefines what you thought you knew about the universe. That’s precisely what happened when the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) turned its gaze towards Jupiter on December 25, 2023, capturing auroras unlike anything seen before.
These weren’t just pretty lights; they were dynamic, intense displays that left scientists “scratching thier heads” adn rewriting the textbooks on planetary auroras. What secrets do these celestial light shows hold, and what can they tell us about the forces shaping our solar system?
Unveiling the Unexpected: JWST’s Christmas Day Finding
Jonathan nichols, a planetary aurora specialist at the University of Leicester, described the experiance as being “blown away.” The initial expectation was to observe auroras that faded in and out gradually, perhaps over fifteen minutes or so. Instead, the entire auroral region was “fizzing and popping with light,” changing sometimes within seconds.
This rapid variability was a complete surprise, challenging existing models of how Jupiter’s auroras behave.It’s like expecting a slow,gentle snowfall and instead witnessing a blizzard of light.
Swift Fact: Jupiter’s auroras are hundreds of times brighter than those on Earth, making them visible even from vast distances.
the Power of collaboration: JWST and Hubble Team Up
The JWST’s observations were further enhanced by simultaneous data collected by the Hubble Space Telescope. By combining the infrared capabilities of JWST’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) with Hubble’s ultraviolet sensors, scientists gained a more complete picture of Jupiter’s auroras.
However, this collaboration also revealed a perplexing mystery: some of the brightest light observed by JWST had no corresponding feature in Hubble’s images. This discrepancy has sparked intense debate and further examination into the underlying mechanisms driving these auroras.
The Infrared Advantage: Seeing the Unseen
JWST’s ability to observe in the infrared spectrum is crucial for studying jupiter’s auroras.Infrared light can penetrate the planet’s hazy atmosphere, revealing details that are invisible to telescopes operating in visible or ultraviolet light. This allows scientists to study the composition, temperature, and dynamics of the auroral regions with unprecedented precision.
think of it like using night-vision goggles to see in the dark. JWST’s infrared vision allows us to see the hidden features of Jupiter’s auroras, revealing a world of complexity and dynamism.
Why Study Jupiter’s Auroras? Unlocking the Secrets of Space Weather
Understanding Jupiter’s auroras is not just about admiring pretty lights. These auroras are a direct result of the interaction between Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field and the solar wind, a stream of charged particles constantly emitted by the Sun.
By studying these interactions, scientists can gain valuable insights into the fundamental processes that govern space weather, which can have notable impacts on earth, affecting everything from satellite communications to power grids.
Space Weather and Earth: A Critical Connection
Severe space weather events, such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections, can disrupt our technological infrastructure and even pose risks to astronauts in space. Understanding how these events interact with planetary magnetic fields is crucial for developing better forecasting models and mitigation strategies.
Jupiter, with its immense magnetic field, serves as a natural laboratory for studying these interactions on a grand scale. By learning how Jupiter’s magnetic field responds to the solar wind, we can better understand and prepare for similar events that could impact Earth.
The Mystery deepens: Unexplained Brightness and Future Research
The fact that JWST observed shining auroral features that were not visible to Hubble raises fundamental questions about the processes driving these light shows. What is causing this discrepancy, and what does it tell us about the composition and dynamics of Jupiter’s atmosphere?
Scientists are now exploring several possible explanations, including variations in the energy and composition of the particles precipitating into Jupiter’s atmosphere, and also differences in the sensitivity of the two telescopes to different wavelengths of light.
Possible Explanations: A Scientific Detective Story
One hypothesis is that the bright features observed by JWST are caused by high-energy particles that emit primarily in the infrared spectrum.These particles might potentially be accelerated by specific processes within Jupiter’s magnetosphere, leading to localized regions of intense infrared emission.
Another possibility is that the composition of Jupiter’s atmosphere varies significantly in the auroral regions, leading to differences in the way it interacts with the incoming particles. further research is needed to determine the precise cause of the observed discrepancies.
Expert Tip: Follow the research! Keep an eye on publications in journals like Nature communications for the latest findings on Jupiter’s auroras.
Future Developments: What’s Next for Jupiter Research?
The JWST’s observations of Jupiter’s auroras are just the beginning.These initial findings have opened up a new window into the dynamics of this giant planet, and future research promises to reveal even more secrets.
Scientists are planning to use JWST to conduct further observations of Jupiter’s auroras,focusing on different wavelengths of light and different regions of the planet. they also hope to coordinate these observations with other telescopes, both on Earth and in space, to obtain a more thorough picture of the auroral phenomena.
The Juno Mission: A Complementary Perspective
NASA’s Juno spacecraft,which is currently orbiting Jupiter,provides a complementary perspective on the planet’s auroras. Juno is equipped with instruments that can measure the magnetic fields and charged particles in jupiter’s magnetosphere,providing valuable context for interpreting the JWST observations.
By combining the data from JWST and Juno, scientists can gain a more complete understanding of the complex interactions between Jupiter’s magnetic field, atmosphere, and the solar wind.
The Broader implications: Understanding Planetary Magnetospheres
The study of Jupiter’s auroras has broader implications for our understanding of planetary magnetospheres in general. Magnetospheres are the regions of space surrounding planets that are dominated by their magnetic fields. These regions protect planets from the harmful effects of the solar wind and play a crucial role in shaping their atmospheres.
by studying the magnetospheres of different planets, including Jupiter, Earth, and even exoplanets orbiting other stars, scientists can gain insights into the fundamental processes that govern the evolution and habitability of planetary systems.
Exoplanet Auroras: A Search for Habitable Worlds
The detection of auroras on exoplanets could be a key indicator of their habitability. Auroras are a sign that a planet has a magnetic field,which can protect its atmosphere from being stripped away by the solar wind. A stable atmosphere is essential for maintaining liquid water on the surface, which is considered a prerequisite for life as we know it.
Future telescopes, such as the Extremely Large Telescope (ELT) currently under construction in Chile, may be able to detect auroras on exoplanets, providing valuable clues about their potential to harbor life.
FAQ: yoru Questions About jupiter’s Auroras Answered
here are some frequently asked questions about Jupiter’s auroras, based on the latest research and expert insights:
What causes auroras on Jupiter?
auroras on Jupiter are caused by the interaction between the planet’s powerful magnetic field and charged particles from the solar wind and Jupiter’s own moons, particularly Io. These particles are accelerated along Jupiter’s magnetic field lines and collide with atoms and molecules in the planet’s atmosphere, causing them to emit light.
How are Jupiter’s auroras different from Earth’s auroras?
Jupiter’s auroras are much more powerful and dynamic than Earth’s auroras. They are also influenced by different factors, such as the planet’s rapid rotation and the presence of volcanic moons like Io. Additionally, Jupiter’s auroras emit light across a wider range of the electromagnetic spectrum, including infrared, which is not typically seen in Earth’s auroras.
Why are scientists so interested in studying Jupiter’s auroras?
Studying Jupiter’s auroras provides valuable insights into the fundamental processes that govern space weather and planetary magnetospheres. By understanding how Jupiter’s magnetic field interacts with the solar wind,scientists can better predict and prepare for similar events that could impact Earth. Additionally, the study of jupiter’s auroras can definitely help us understand the potential habitability of exoplanets.
What role does the James Webb Space Telescope play in studying Jupiter’s auroras?
The James Webb Space Telescope’s infrared capabilities allow scientists to study Jupiter’s auroras in unprecedented detail. infrared light can penetrate Jupiter’s hazy atmosphere, revealing features that are invisible to telescopes operating in visible or ultraviolet light. this allows scientists to study the composition, temperature, and dynamics of the auroral regions with greater precision.
What are some of the mysteries surrounding Jupiter’s auroras?
One of the biggest mysteries surrounding Jupiter’s auroras is the discrepancy between the observations made by JWST and Hubble. JWST observed bright auroral features that were not visible to Hubble,raising questions about the processes driving these light shows. Scientists are also working to understand the rapid variability of Jupiter’s auroras and the role of jupiter’s moons in shaping their behavior.
Pros and cons: The benefits and Challenges of Studying Jupiter’s Auroras
Like any scientific endeavor, the study of jupiter’s auroras has both its benefits and challenges:
Pros:
- Improved understanding of space weather: Studying Jupiter’s auroras can help us better understand and predict space weather events that could impact Earth.
- Insights into planetary magnetospheres: Jupiter’s magnetosphere serves as a natural laboratory for studying the fundamental processes that govern these regions.
- Potential for exoplanet discovery: The detection of auroras on exoplanets could be a key indicator of their habitability.
- Advancement of telescope technology: the study of Jupiter’s auroras pushes the limits of telescope technology, leading to new innovations and discoveries.
Cons:
- Distance and accessibility: jupiter is a long way away, making it tough and expensive to send spacecraft and telescopes to study it.
- Complex data analysis: The data collected from Jupiter’s auroras.