Beyond the Image: Unveiling the Future of Space Observation
Table of Contents
- Beyond the Image: Unveiling the Future of Space Observation
- Beyond the Pretty Pictures: Space Observation’s Next Chapter with Dr. Aris Thorne
What if the images we’re seeing from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) are just the tip of the iceberg? The recent revelations about Jupiter’s auroras, hidden black holes in M83, adn the dying star in NGC 1514 are not just pretty pictures; they’re clues to unlocking the universe’s deepest secrets. But what happens *next*?
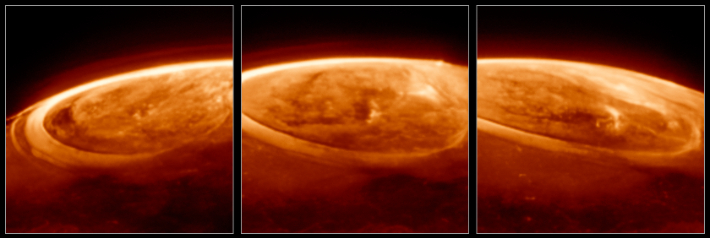
Jupiter’s Everlasting Light Show: Predicting Solar Weather’s Impact
NASA’s stunning images of Jupiter’s auroras, far grander than our own Northern Lights, raise a critical question: how does solar weather *really* impact planetary atmospheres? The key lies in understanding the interaction between Jupiter’s magnetosphere and the solar wind, a stream of charged particles constantly emitted by the sun.
The Io Connection: Volcanic Activity as a Cosmic Driver
Did you know? Jupiter’s moon Io, riddled with active volcanoes, plays a meaningful role in fueling these auroras. Particles ejected from Io are captured by Jupiter’s magnetic field, accelerated to high speeds, and then collide with the planet’s atmosphere, creating the dazzling display. Future research will focus on predicting how changes in Io’s volcanic activity might affect jupiter’s auroral intensity and patterns.
Black Hole Hide-and-Seek: Rewriting Galaxy Evolution
The discovery of a hidden black hole in the M83 galaxy challenges our understanding of how galaxies evolve. For years, astronomers believed M83 lacked an active galactic nucleus (AGN), the telltale sign of a supermassive black hole actively consuming matter.The JWST’s mid-infrared observations revealed ionized neon gas, a smoking gun pointing to a previously undetected black hole.
Implications for the Milky Way: Are We Missing Somthing?
This discovery has profound implications for our own Milky Way galaxy. Could there be dormant or obscured black holes lurking in our galactic neighborhood, influencing the distribution of stars and gas? Future surveys using advanced telescopes will be crucial for identifying these hidden giants and refining our models of galaxy formation.
NGC 1514: Decoding the Death Throes of a Star
The “crystal Ball Nebula,” NGC 1514, offers a glimpse into the final stages of a star’s life. As a star exhausts it’s nuclear fuel, it sheds its outer layers, creating a planetary nebula.The JWST’s infrared observations have revealed intricate ring structures and an hourglass shape within NGC 1514, providing valuable insights into the complex processes that shape these celestial objects.
Dust as a Time Capsule: Unraveling Stellar Evolution
The analysis of dust composition within NGC 1514, including carbon, silicone, and oxides, is especially exciting. This details acts like a time capsule, revealing the elements forged within the dying star and how they are returned to the universe, enriching the interstellar medium for future generations of stars and planets. This is crucial for understanding the cycle of matter in the cosmos.
The Future is Infrared: A New Era of Discovery
The James Webb Space Telescope’s success highlights the importance of infrared astronomy. By observing the universe in infrared light, we can peer through dust clouds, uncover hidden objects, and study the faint light from distant galaxies. This is revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos and paving the way for future generations of space telescopes.
What other secrets are waiting to be uncovered? Only time, and continued exploration, will tell. Share your thoughts in the comments below!
Beyond the Pretty Pictures: Space Observation’s Next Chapter with Dr. Aris Thorne
Keywords: James Webb Space Telescope, JWST, space observation, jupiter auroras, black hole, galaxy evolution, star formation, planetary nebula, infrared astronomy, space weather, astronomical research
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is delivering breathtaking images of the cosmos, but are we truly grasping the depth of its discoveries? To delve deeper, we spoke with dr. Aris Thorne,a renowned astrophysicist specializing in stellar evolution and galactic dynamics,to unpack the latest findings and explore what the future holds for space observation.
Time.news: Dr.Thorne, thank you for joining us. The JWST images of Jupiter’s auroras are stunning. What’s the real importance beyond the visual spectacle?
Dr. Aris Thorne: The auroras are indeed captivating,but their true value lies in what they reveal about the interaction between Jupiter’s magnetosphere and the solar wind. These observations are critical for understanding space weather’s impact on planetary atmospheres. It’s not just about Jupiter; it helps us model how solar activity affects Earth and other planets.
Time.news: the article mentions the role of Io’s volcanic activity in fueling Jupiter’s auroras. How does a volcanic moon contribute to such a planetary-scale phenomenon?
Dr. Aris Thorne: Io is essentially a giant, cosmic sprinkler emitting charged particles into Jupiter’s magnetic field.These particles are accelerated to incredible speeds and then slam into Jupiter’s atmosphere, generating the auroras. Changes in Io’s volcanic activity directly influence the intensity and patterns of the auroras, making it a critical factor in our models.Future research focusing on Io will be vital.
Time.news: What advice would you give to our readers who want to stay informed about advancements in space weather forecasting?
Dr.Aris Thorne: Absolutely! Keep an eye on upcoming missions specifically designed to study Jupiter’s magnetosphere.These missions will provide invaluable data, leading to more accurate space weather forecasts. This is crucial not just for scientific curiosity, but for protecting our satellites and astronauts from harmful radiation.
Time.news: the discovery of a hidden black hole in M83 seems to be a game-changer. Why is this such a significant finding?
Dr. Aris Thorne: for years, astronomers believed M83 lacked an active galactic nucleus (AGN), the typical sign of a supermassive black hole actively feeding. The JWST’s infrared capabilities allowed us to see through the dust and gas, revealing ionized neon gas, a clear indicator of a previously undetected black hole. This forces us to rethink how galaxies evolve and whether we’ve overlooked black holes in other galaxies, including our own.
Time.news: You mentioned our own Milky Way. Could there be similar hidden black holes lurking in our galactic neighborhood? What are the implications for the Milky Way?
Dr. Aris Thorne: It’s a real possibility. If M83 had a hidden black hole, the Milky Way could have dormant or obscured black holes influencing the distribution of stars and gas in ways we haven’t fully understood. Future surveys using advanced telescopes are essential for identifying these hidden giants and ultimately refining our models of galaxy formation.
Time.news: Let’s shift our focus to NGC 1514, the “Crystal Ball nebula.” How does analyzing the dust composition in these dying stars help us understand stellar evolution?
Dr. Aris Thorne: NGC 1514 provides a unique prospect to study the late stages of a star’s life. The dust expelled from the dying star acts like a time capsule, revealing the elements forged within its core – carbon, silicone, oxides, and more.By analyzing this dust, we can understand how stars create these elements and how they are returned to the interstellar medium, enriching it for future generations of stars and planets. It’s crucial for understanding the cycle of matter in the cosmos.
Time.news: The article stresses the importance of infrared astronomy. What makes it so powerful compared to other forms of observation?
Dr. Aris Thorne: infrared light has a unique ability to penetrate dust clouds that obscure visible light. This allows us to see hidden objects like forming stars, distant galaxies, and even the hearts of active galactic nuclei. The JWST’s success underscores that infrared astronomy is revolutionizing our understanding of the universe and paving the way for future generations of even more powerful space telescopes.
Time.news: Dr. Thorne, thank you for sharing your expertise with us. Any final thoughts for our readers?
Dr. Aris Thorne: The JWST is opening up entirely new avenues of discovery. this is a golden age for astronomy, and the discoveries being made are fundamentally changing our understanding of the universe. Stay curious, follow the progress, and remember that every breathtaking image is just one piece of a much larger, awe-inspiring puzzle.