Scientists have discovered that love originates in a specific part of the brain, not the heart.
The word ‘love’ is used in many contexts, from sexual affection between lovers to between parents and children, pets, and nature. Of the various types of love, parental love for children appears to be the most powerful.
Researchers at Aalto University in Finland have discovered that the same word, love, activates different parts of the brain depending on the type of human experience.
According to the research results announced on the 26th (local time) in the international academic journal ‘Cerebral Corte’, the research team had 55 experimental participants (all parents of children) who said they had a love object tell short stories about six types of love – love for children, lovers, friends, strangers, pets, and nature – through acting by professional actors.
For example, participants were presented with scenarios that prompted them to recall a memory of seeing a newborn for the first time, such as “You see your newborn baby for the first time. He is soft, healthy, and full of life. You feel the greatest wonder of your life, and you love this little being.”
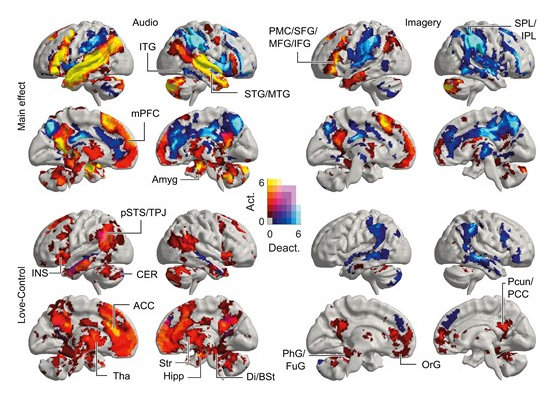
While they listened to and thought about six different types of love stories, their brain activity was measured using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). Their brain responses to feelings of love were compared to their responses when they heard neutral stories in which nothing happened.
Researchers have found that love for children triggers the most intense brain activity, followed by romantic love.
“When imagining parental love, there was activation deep in the brain’s reward system, in the corpus striatum region,” said co-author Professor Pärttyli Rinne, explaining that this intense brain activity was not seen in other types of love.
Although the intensity of brain activity varied across types, most activated the same areas of the brain, with some exceptions.
“The activation pattern of love is generated in social situations in the basal ganglia, the midline of the forehead, the precuneus on the side of the back of the head, and the temporoparietal junction,” added Professor Linnaeus.

Interestingly, all types of love between people activated the same areas of the brain, regardless of the level of intimacy in the relationship, but the intensity of activation varied. The study found that compassionate love for a stranger was less rewarding and elicited less brain activity than love in a close relationship.
Love for nature activated the brain’s reward system and visual areas, but not social brain areas, suggesting that brain activity in response to feelings of love is influenced not only by the familiarity of the object, but also by whether it is a human, another species, or nature.
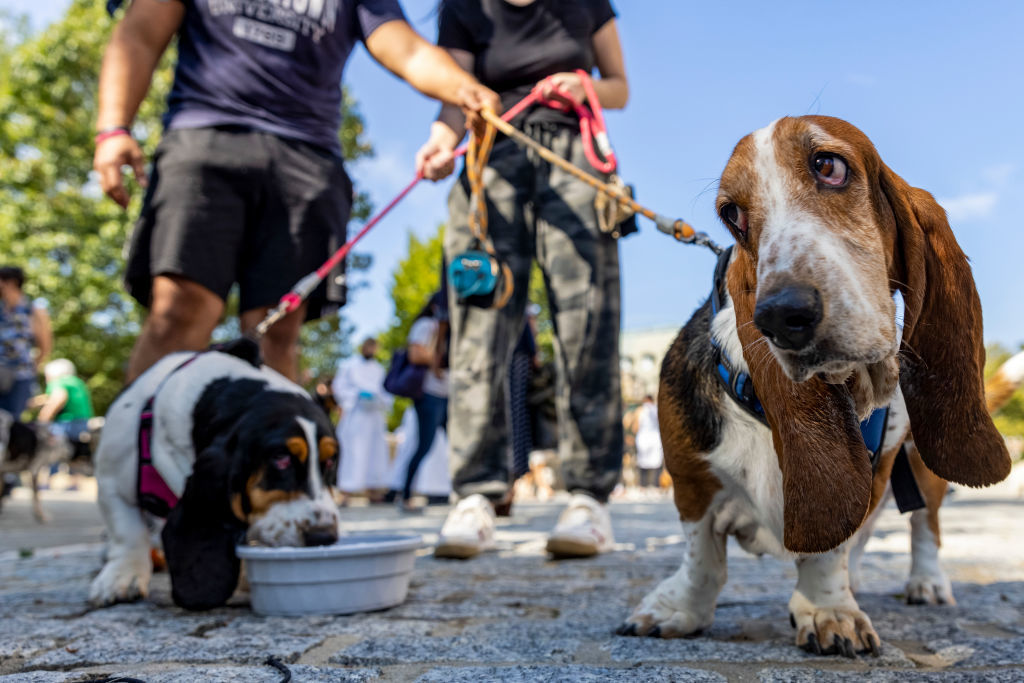

When people imagine spending time with their furry friend, brain regions associated with social emotions are activated more than when they think about nature. EEG can be used to determine whether a person is a pet owner.
“When we look at love for pets and the brain activity associated with it, the brain regions associated with sociality statistically reveal whether a person is a pet owner or not. In pet owners, these regions are more active than in non-pet owners,” said Professor Linnaeus.
Scientists hope the study could be used to better treat attachment disorders, depression and relationship problems.
참고자료-Six types of loves differentially recruit reward and social cognition brain areas. Cerebral Cortex, 34(8).
(
Reporter Park Hae-sik, Donga.com [email protected]
-
- great
- 0dog
-
- I’m sad
- 0dog
-
- I’m angry
- 0dog
-
- I recommend it
- dog
Hot news right now
2024-08-27 11:48:11

