2023-05-30 18:19:47
If you consume too much vitamin D, it can lead to an excess of calcium in the blood. Due to this, various symptoms and signs of toxicity appear, which can negatively affect the general condition. However, neither excessive exposure to sunlight nor the consumption of such foods are possible causes. An overdose of the vitamin is more likely to be due to the increased intake of dietary supplements. In order to prevent possible health risks, you can find out more about the side effects and the necessary measures below.
How can too much vitamin D cause symptoms in the body?
Excessive amounts of the vitamin absorbed through sunlight are not harmful to health since the body breaks down D3 when the skin warms up. In addition, various other non-functional forms of the sun vitamin are also formed from the thermally activated compound. However, vitamin D overdose can cause muscle pain, dizziness, frequent urination, and headaches. This happens especially when you take too much vitamin D through supplementation takes. Other physical symptoms could also include weakness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting.

In worse cases, vitamin D toxicity can even lead to kidney or bone problems or cause kidney stones. Otherwise, it is an important nutrient that helps the body absorb calcium, which helps build strong bones. Given the symptoms described above, the vitamin also plays a crucial role in the function of the immune system, the nervous system and the muscles. On the other hand, a vitamin D deficiency could lead to mental disorders such as depression.
What is the current recommended daily dose of vitamin D?

For the majority of people, supplementing with the vitamin can be beneficial. In this way, they can increase the vitamin content in the blood to a sufficient level. This can be achieved either by sunbathing or by changing your diet, or by taking supplements as recommended by a doctor. While a deficiency in this nutrient is a very common problem, it would also be possible to have too much vitamin D in the blood. So-called hypervitaminosis can lead to the serious health risks described above. However, many people try to self-medicate, which often leads to overdose.

When it comes to the current daily dose of vitamin D recommended by health experts, it is currently 600 IU per day for adults under the age of 70 and 800 IU for the elderly. A safe upper limit is usually up to 4,000 IU per day. However, daily doses up to 10,000 IU have not been shown to be toxic. In most cases, however, it is actually about excessively taken supplements, which accordingly led to significantly higher amounts being absorbed by the body. However, these are rare cases because it is not always easy to ingest toxic levels of vitamin D.
What are the signs of too much vitamin D to look out for?

So there is a chance of suffering from certain symptoms of intoxication if you overdose on vitamin D. These are primarily linked to the metabolism, which can include hypervitaminosis D, hypercalcaemia, hypercalciuria and hyperphosphataemia. However, the latter two are not consistent findings regarding vitamin D toxicity, although they are common. But what can happen to the body if you take too much vitamin D? In addition to the symptoms described, some signs of overdose include, for example, constipation, dehydration, disorientation, fatigue, high blood pressure, irritability, thirst or tinnitus.

As for hypercalcemia, the normal blood calcium level should be between 8.8 mg/dl and 10.8 mg/dl. Values between 10.5 and 13.9 mg/dl indicate the symptoms as mild to moderate, while values between 14.0 and 16.0 mg/dl are considered a hypercalcemia crisis. Hypercalcemia from excess vitamin D could be treated with steroids, although eliminating the source of the excess vitamin is also crucial. Vitamin D’s fat solubility means that toxic effects can linger months after exogenous supplementation or ingestion has ceased.
What are the risks for kidneys and other organs from too much vitamin D?
Another health hazard from excess vitamin D intake and hypercalcemia can also lead to kidney problems or even kidney damage. Since this also increases the absorption of calcium, it can cause kidney stones to form. There is also evidence that vitamin D overdose can also lead to more serious, long-term kidney damage. In some cases, the deposits in the kidneys can lead to what is known as nephrocalcinosis, which can cause permanent kidney damage or even kidney failure.

While getting enough vitamin D is essential for bone health, too much can actually be detrimental. Some research has found that too much vitamin D can impair the effect of vitamin K2 can. This is a nutrient that helps retain calcium in the bones. Other health risks cannot be ruled out either, with long-term toxicity even leading to pancreatic cancer, cardiovascular problems and falls leading to fractures in the elderly.
How can vitamin D toxicity be prevented?

If you are deficient in vitamin D, you can start taking supplements to help relieve any symptoms you may have, such as seasonal depression. However, it becomes problematic if you overdo it or think that taking a larger amount would have more positive effects. To prevent toxicity, the tolerable upper intake levels for vitamin D have been established as follows:
Age recording (IE)
0-6 Fun 1000
7-12 Fun 1500
1-3 years. 2500
4-8 years 3000
≥9 years 4000
Pregnant 4000
The body produces vitamin D when exposed to the sun, but many people don’t get enough of it due to various factors. In most cases, you can meet all of your sun vitamin needs naturally, without supplementation, through exposure to the sun and diet. Regular walks outside with exposed extremities can also boost vitamin D production. However, if you are going to be out in the sun for more than 20 minutes, use sunscreen on your skin.
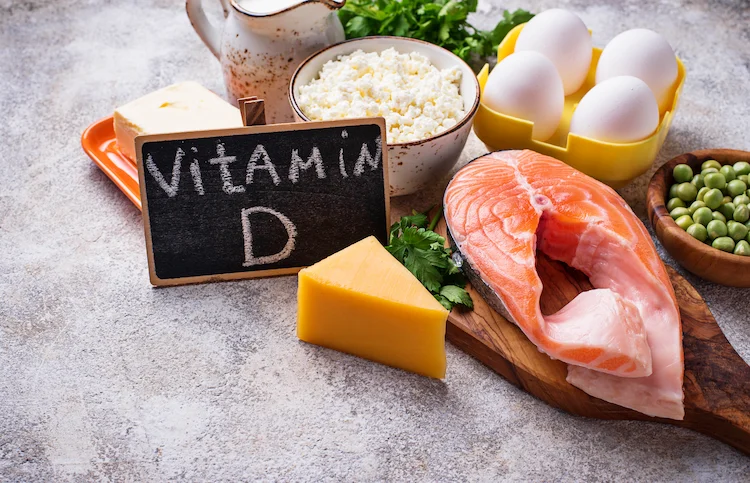

Eating foods that are naturally high in vitamin D or fortified with this nutrient can also help. These include egg yolks, fortified milk, yogurt or juice, cheese, fatty fish like salmon or tuna, and offal like liver. If you decide to take a vitamin D supplement to make up for a deficiency or because you are unable to get an adequate amount through sunlight and diet, always follow your doctor’s advice and do not take more than the recommended amounts.
#vitamin #risks
