CITY, Month 15, 2024 – The landscape of liver health is shifting, and the trends are alarming. Recent data paints a grim picture: deaths from alcohol-related liver disease are surging, with women, young adults, and Native populations bearing the brunt of this increase.
A Sobering Rise in Deaths
Alcohol-related liver disease deaths have doubled in two decades, impacting women, young adults, and Indigenous communities the most.
- Deaths from alcohol-related liver disease have doubled in the past 20 years.
- Women and young adults are experiencing a rapid increase in these deaths.
- Native populations are disproportionately affected.
Why are alcohol-related liver disease deaths increasing, particularly among women and young adults? A comprehensive analysis reveals a concerning trend: the number of deaths related to alcohol-associated liver disease has doubled over the past two decades.
The data shows a significant rise in mortality rates. While the increase is concerning across the board, certain demographics are experiencing a more rapid escalation. These include women, young adults, and Indigenous populations, who are facing disproportionately high rates of alcohol-related liver disease deaths.
Reader question: What steps can individuals take to assess their personal risk of developing alcohol-related liver disease, and what resources are available for early detection and prevention?
Disparities and Demographics
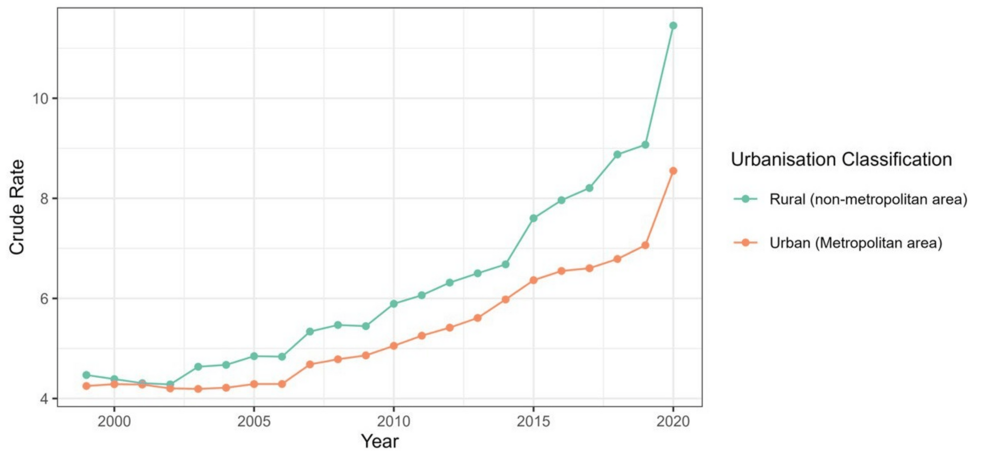
The study highlights the complex interplay of factors contributing to these disparities. While alcohol consumption patterns play a role, other elements such as access to healthcare, socioeconomic status, and underlying health conditions also contribute to the increased risk. Urban versus rural differences also show disparities.
For example, a study analyzing data over a 22-year period in the United States revealed variations in mortality rates between urban and rural areas. This suggests that geographic location can influence both the risk factors and the outcomes associated with alcohol-related liver disease.
Did you know? Even moderate alcohol consumption can contribute to liver damage over time, especially when combined with other risk factors such as obesity or certain medications.
The Impact on Specific Groups
Women are experiencing a particularly sharp increase in alcohol-related liver disease deaths. Experts suggest that differences in metabolism, body composition, and hormonal factors may make women more vulnerable to the damaging effects of alcohol.
Young adults are also facing a rising risk. This could be linked to changing drinking habits, increased alcohol consumption, and a lack of awareness about the potential health consequences. Data also reveals a rise in liver disease mortality among Native populations.
Did you know? Alcohol-related liver disease includes conditions like alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer.
Understanding the Risks
The rise in alcohol-related liver disease deaths underscores the need for increased awareness and proactive measures. It’s vital to understand the risks associated with excessive alcohol consumption and to take steps to protect liver health.
Addressing this issue requires a multi-pronged approach. This includes public health campaigns to educate the public about safe drinking guidelines, expanded access to treatment for alcohol use disorders, and policies that reduce alcohol-related harm.
Understanding and Mitigating risk: A Closer Look
To answer the reader’s question, it’s crucial to understand how alcohol damages the liver and what steps can be taken for prevention. The liver’s primary role is processing everything we consume, including alcohol [[3]]. Excessive alcohol consumption overworks the liver,leading to a range of conditions collectively known as alcohol-associated liver disease (ALD) [[2]].
Alcohol-related liver disease stages include fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and cirrhosis, the most severe form. This advanced stage is often irreversible [[1]].Early detection and preventative measures are vital. The following sections help you assess personal
Table of Contents