2023-04-26 20:30:55
Thousands of years ago, humans observed that physical phenomena, such as the seasons, were associated with the cycles followed by the stars. They thought that if they could understand how the sky worked, perhaps they could predict the designs of man. Thus, the belief that the heavens influenced people’s lives contributed to the development of astronomy.
The astronomical origin of astrology
While Ptolemy’s Almagest was a book on what we now think of as astronomy, his Tetrabiblos It’s astrology. For Ptolemy, astronomy and astrology are complementary, and he clarifies this in the introduction to the Tetrabiblos:
“The first [se refiere a la Astronomía] it deals with that which we apprehend from the aspects of the motions of the Sun, the Moon, and the stars in relation to each other and to the Earth, as they occur from time to time; the second is that in which, by means of the natural character of these same aspects, we investigate the changes that they produce in what surrounds them.”
In Chapter 2 he gives arguments to justify the influence of heaven in the future of people:
“Because the Sun, along with the environment, is always affecting everything on earth in some way. […]. The farmers and shepherds […]from the winds that prevail at the time of fertilization and sowing of the seed, the quality of what will result […]. If, then, a man accurately knows the motions of all the stars, the Sun and the Moon, so that neither the place nor the time of any configuration of his escapes his attention […]; And if he is able to determine, in view of all these data, both scientifically and by correct conjecture, the distinguishing mark of quality resulting from the combination of all factors, what prevents him from being able to say on each occasion given the characteristics of the air at from the relations of the phenomena at the moment, for example, that it will be warmer or more humid? Why can’t he, too, with respect to an individual man, perceive the general quality of temperament in his environment at the time of his birth? […] using the fact that this or that environment is in tune with this or that temperament and is favorable to prosperity, while another is not so in tune and leads to harm?
It is reminiscent of scientific reasoning, although today we know that astrology has no scientific foundation.
The birth of the constellations
The idea of constellation (groups of stars imaginatively associated with figures) was systematized in Mesopotamia. This can be seen in a set of tablets whose origin dates back to 1,000 years BCE, known as MUL.APIN.
British Museum
In ancient Egypt, the position of some stars served as a reference for agricultural activities. For example, the heliacal appearance of Sirius (Sopdet or Sothis) coincided with the maximum rise of the Nile.
In classical Greek texts mention is made of constellations. For example, a passage from the Odyssey (c. VIII BC) narrates that Ulysses is guided by the Big Dipper to return to Ithaca.
constellations and zodiac signs
A constellation was the set of stars that formed the drawing that gave the constellation its name (imagine the stars as dots on a piece of paper joined with lines). The other nearby stars were considered stars associated with the constellation.
The current definition of a constellation includes all the stars within an area of the celestial sphere. These were defined less than a century ago, in 1930, by the International Astronomical Union.
The zodiacal constellations are those included in a band of the celestial sphere through which the ecliptic passes (apparent path followed by the Sun in the celestial sphere throughout a year, seen from Earth). Behind the zodiacal constellations are the zodiacal signs, whose names derive from the names of animals. Zodiac meant in Greek animal wheel (whose origin dates back to Mesopotamia).

Source: Prepared by the author from the Almagest.
The ancient Greeks already knew Ophiuchus
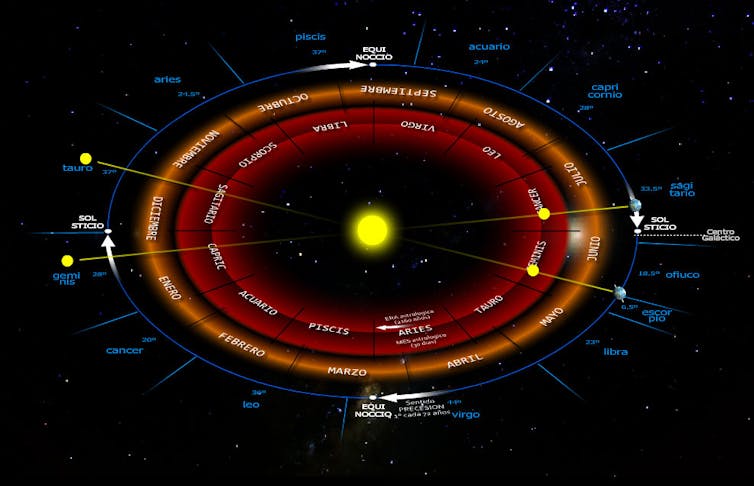
Around the 5th century BCE, the position of the zodiac constellations coincided with the zodiac sign of the same name, although there is no direct correspondence as constellations and signs occupy different extensions. Actually, there are 13 constellations that pass through the ecliptic. The thirteenth is Ophiuchus and the Greeks knew it.
The division into 12 equal sectors probably has its origin in Mesopotamia, and was done this way to make them coincide with their months.
To establish the position of the zodiacal signs, the sign of Aries (♈︎ 0º) is taken as the beginning, which corresponds to the Aries point, coinciding with the spring equinox (in the northern hemisphere).

However, the coincidence of signs and constellations in the same position was for a relatively long time. Due to the precession of the equinoxes discovered by Hipparco, the position of the stars does not follow an annual cycle but they move with respect to the zodiacal signs, approximately 1º per century.
The Ptolemy Catalog
Claudius Ptolemy (Alexandria, 2nd century) collected the Babylonian tradition and previous astronomers, in particular Hipparco, possibly the most influential astronomer of antiquity. In its Mathematical Syntax o Almagesto, develops a mathematical model that allows calculating the position of the planets with respect to the zodiacal signs (which is not the same as zodiacal constellations) that includes the position of more than 1,000 stars. Recently, a palimpsest has found a detailed description of the meteoroscope (a type of armillary sphere) that he used to measure the positions of the stars.
Ptolemy’s catalog contains 48 constellations (those then visible from Alexandria). For each constellation the stars that form it are included, with a description, their position in ecliptic coordinates and the magnitude (apparent luminosity). The ecliptic longitude is expressed in degrees, referred to the corresponding zodiacal sign, for example: the Regulus star in the Almagesto It has longitude: ♌︎ 2 ½, which indicates that it is 2º 30′ from the beginning of the sign of Leo (♌︎). The same constellation is usually distributed among more than one sign.

Source: Prepared by the Author from the Almagest.
The practice of referring the positions with respect to the zodiacal signs continued until Copernicus (late 16th century) and this is sometimes forgotten, even in recent publications.
Should we check the dates of the horoscopes?
This year, as has often happened for several years, the hoax spread that NASA was going to change the dates of the zodiac signs and that it would give entry to a new sign, Ofiuco (⛎). “Scientific explanations” appeared in various media about the alleged mistake that astrologers made when using dates from more than 2,000 years ago in horoscopes. But it was not like that. Astrologers/astronomers distinguished between zodiacal signs and constellations. Among other reasons, they had a practical justification: the zodiacal signs were the ones that were believed to influence people, since they were the ones that marked the climatic seasons.
Wikipedia (Creative Commons 4.0)
Currently, the zodiac signs, which is the reference for horoscopes, are displaced by almost a month with respect to the constellations, and Ofiuco is in the zodiac band, although it is still not considered a zodiac sign.
In any case, there is no need to worry about being born under one sign or another. Since the 17th century, astrology has come to be considered a false belief. Somehow it had stimulated the development of astronomy but its time had passed.
#astrology #contributed #development #astronomy
