Rare Genetic Deficiency Linked to Severe Pregnancy Complications: A Case Study
Table of Contents
A rare genetic condition, CYP24A1 deficiency, has been identified as the cause of dangerously high calcium levels and vitamin D excess in a pregnant woman, highlighting a previously underrecognized risk during pregnancy. The case, detailed in a recent report, underscores the importance of considering this deficiency in expectant mothers presenting with hypercalcemia and hypervitaminosis D.
The condition, stemming from a mutation affecting the CYP24A1 gene, disrupts the body’s ability to regulate vitamin D metabolism. This disruption can lead to excessive calcium absorption and potentially severe health consequences for both mother and fetus.
Understanding CYP24A1 Deficiency
CYP24A1 deficiency is a rare autosomal recessive disorder. This means an individual must inherit two copies of the mutated gene – one from each parent – to develop the condition. The CYP24A1 enzyme is crucial for breaking down vitamin D into inactive metabolites, preventing toxic buildup. Without sufficient enzyme activity, vitamin D levels can soar, leading to hypercalcemia.
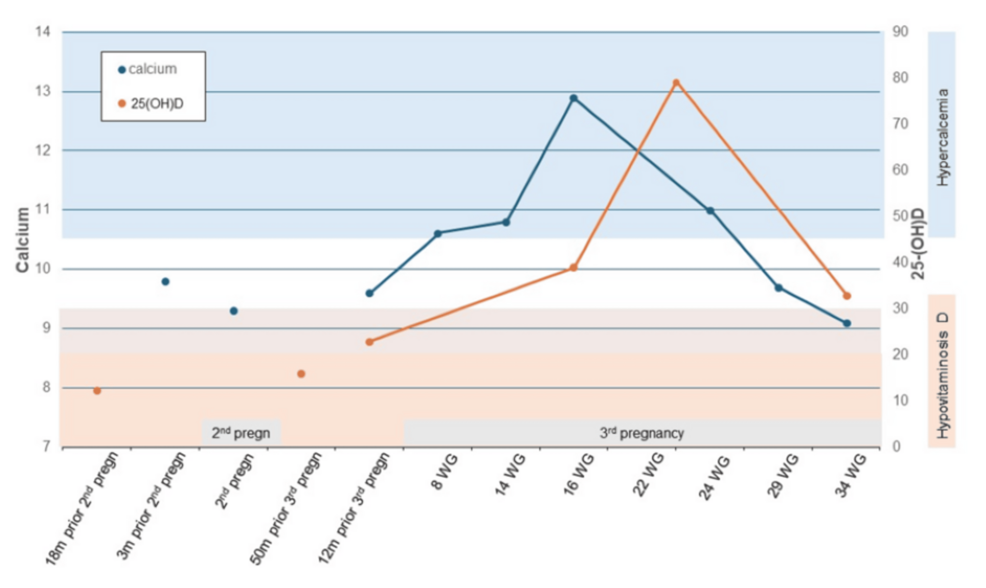
According to the case report, the patient presented with symptoms including nausea, vomiting, and weakness during her pregnancy. Initial investigations revealed significantly elevated calcium and vitamin D levels. “The severity of the hypercalcemia was particularly concerning, posing a risk of cardiac arrhythmias and kidney damage,” one physician stated in the report.
The Case: A Pregnant Woman’s Ordeal
The patient, whose specific details have been anonymized to protect her privacy, was initially suspected of having primary hyperparathyroidism, a more common cause of high calcium levels. However, further genetic testing revealed a homozygous mutation in the CYP24A1 gene, confirming the diagnosis.
The patient’s vitamin D levels were found to be markedly elevated, exceeding normal ranges by a substantial margin. This excess vitamin D was directly linked to the impaired function of the CYP24A1 enzyme. The report details that the patient’s condition required careful management throughout her pregnancy, including dietary modifications and close monitoring of calcium and vitamin D levels.
Implications for Pregnancy and Future Research
This case report is significant because it expands the known spectrum of conditions that can cause hypercalcemia and hypervitaminosis D during pregnancy. Previously, these conditions were often attributed to more common causes.
The report emphasizes the need for clinicians to consider CYP24A1 deficiency in pregnant women presenting with these symptoms, particularly if initial investigations are inconclusive. Early diagnosis is crucial for preventing potentially life-threatening complications.
“This case highlights the importance of genetic testing in complex cases of hypercalcemia, especially during pregnancy,” a senior researcher commented. “It also underscores the need for increased awareness of this rare but serious condition among healthcare professionals.”
Further research is needed to determine the prevalence of CYP24A1 deficiency and to develop optimal management strategies for affected individuals, particularly during pregnancy. . The long-term effects of CYP24A1 deficiency on fetal development also warrant further investigation. This single case serves as a critical reminder of the complexities of vitamin D metabolism and the potential for rare genetic disorders to manifest during pregnancy, demanding vigilance and a broadened diagnostic approach.