“`html
Rare Complication Following Prostate Cancer Spacer Placement: Rectal Ulcer and Bleeding Reported
Table of Contents
A new case report highlights a rare but serious complication associated with the SpaceOAR hydrogel, a spacer used to reduce radiation side effects in men undergoing treatment for prostate carcinoma. The report, published in Cureus, details the development of a rectal ulcer leading to hematochezia – the passage of blood in stool – in a patient following the spacer’s placement. This finding underscores the importance of careful monitoring for gastrointestinal issues in patients receiving this increasingly common intervention.
The SpaceOAR implant is designed to create space between the prostate and the rectum, minimizing radiation exposure to the rectal wall and reducing the risk of long-term side effects like rectal toxicity. While generally considered safe, this case demonstrates a potential, albeit uncommon, adverse event.
Spacer Placement and Initial Recovery
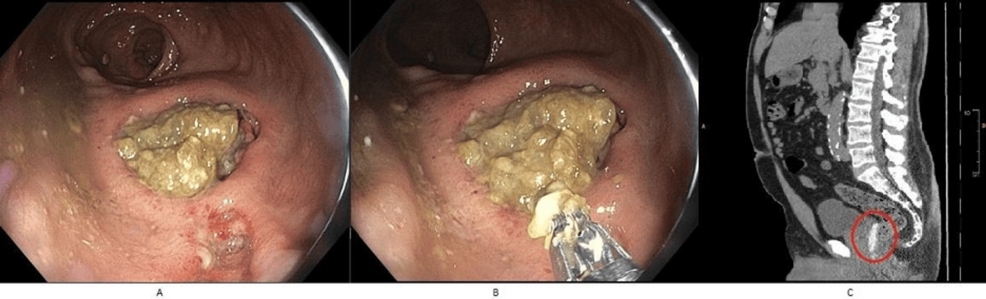
The patient, undergoing radiation therapy for localized prostate cancer, received the SpaceOAR implant without immediate complications. According to the report,the procedure itself was completed successfully,and the patient initially recovered well. Tho, approximately six weeks after the implant was placed, the patient began experiencing rectal discomfort and subsequently noticed blood in his stool.
Further investigation, including a colonoscopy, revealed a significant ulcer in the rectum directly adjacent to were the SpaceOAR hydrogel was positioned. The ulcer was determined to be the source of the hematochezia. “The location of the ulcer strongly suggested a relationship to the presence of the hydrogel,” the report stated.
Investigating the Cause and Treatment
The case report delves into potential mechanisms behind the ulcer development. While the exact cause remains unclear, researchers hypothesize that the hydrogel may have caused localized pressure or irritation to the rectal wall, leading to tissue breakdown and ulceration. Another possibility considered was a localized inflammatory response to the hydrogel material itself.
Treatment involved conservative management, including bowel rest and medication to reduce inflammation.The SpaceOAR hydrogel was eventually removed, and the rectal ulcer gradually healed with continued medical care.The patient’s hematochezia resolved following the removal of the implant and subsequent treatment.
Implications for Prostate Cancer Treatment
This case report adds to the growing body of literature surrounding the SpaceOAR hydrogel and its potential complications. While the benefits of reducing rectal toxicity with the spacer are well-established, clinicians must remain vigilant for unexpected adverse events.
Key takeaways from the report include:
- Awareness: Physicians should be aware of the possibility of rectal ulceration as a potential complication following SpaceOAR placement.
- Monitoring: Close monitoring for gastrointestinal symptoms,such as rectal discomfort or bleeding,is crucial in patients with the implant.
- Prompt Investigation: Any reported symptoms should be investigated promptly with appropriate diagnostic testing, such as colonoscopy.
“This case highlights the need for continued research and careful patient selection when considering the use of SpaceOAR,” one analyst noted.While the risk appears low, the potential for serious complications necessitates a thorough discussion of risks and benefits with patients before proceeding with the procedure. The report emphasizes that while prostate carcinoma treatment options continue to