Axial Seamount: Is an Underwater Volcanic Eruption Imminent Off the US Coast?
Table of Contents
- Axial Seamount: Is an Underwater Volcanic Eruption Imminent Off the US Coast?
- The Location and the Threat
- A History of Eruptions and Monitoring
- Potential Impacts: Marine Life and Deep-Sea Exploration
- The scientific Perspective: Excitement, Not Alarm
- the Broader Context: Underwater Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
- FAQ: Understanding Axial Seamount
- What is Axial Seamount?
- Where is Axial Seamount located?
- when did Axial Seamount last erupt?
- How do scientists monitor Axial Seamount?
- Will the eruption of Axial Seamount affect humans?
- What are the potential impacts on marine life?
- Could the eruption cause a tsunami?
- What does the future hold for Axial Seamount?
- Pros and Cons of Monitoring Underwater Volcanoes
- The Future of Underwater Volcanism Research
- Interview: Decoding the impending Axial Seamount eruption with Dr.Evelyn Reed
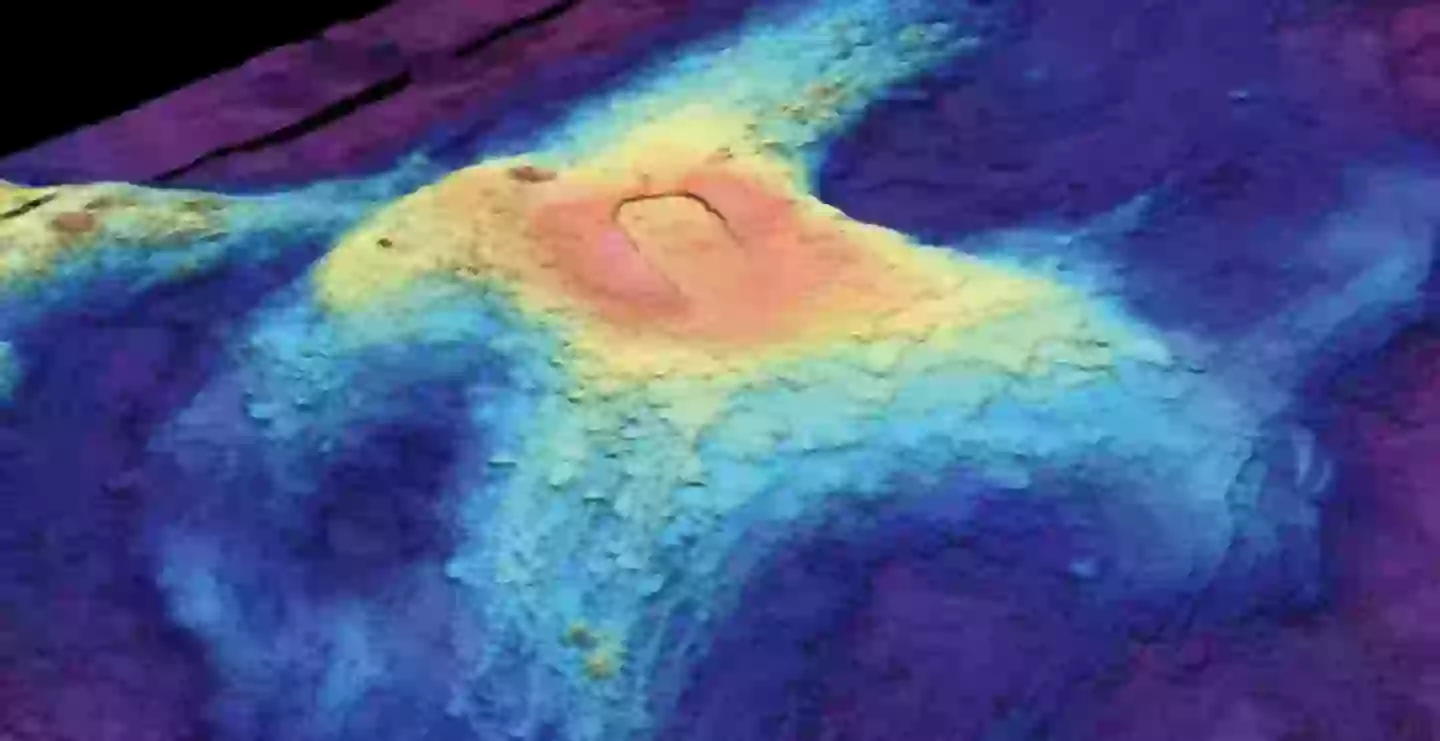
Imagine a world where the earth beneath the ocean floor rumbles, hinting at a powerful eruption. That world might be closer than you think. Scientists are closely watching Axial Seamount, a major underwater volcano located about 300 miles off the coast of Oregon, and signs suggest it coudl erupt sooner rather than later [[1]].
The Location and the Threat
Axial Seamount sits nearly 5,000 feet below the surface of the Pacific Ocean. This isn’t some dormant giant; it’s an active volcano that has been triggering a significant number of earthquakes in recent weeks, signaling that magma is pushing its way towards the surface [[1]]. While volcanic eruptions often conjure images of Pompeii-like devastation, scientists believe this particular eruption is unlikely to directly impact humans [[1]].
A History of Eruptions and Monitoring
Scientists have been diligently monitoring Axial Seamount, especially since its last eruption in 2015. The current activity levels are mirroring those observed leading up to that event [[1]]. william Wilcock, a professor and marine geophysicist at the University of Washington, suggests the eruption could happen “as early as tomorrow,” while also acknowledging the inherent unpredictability of volcanic activity [[1]]. A more conservative estimate places the eruption sometime later this year or in early 2026 [[1]].
The 2015 Eruption: A Case Study
The 2015 eruption of Axial Seamount provides valuable data for predicting future events. That eruption triggered approximately 8,000 earthquakes and caused the ocean floor to sink by about eight feet [[1]]. This subsidence highlights the dynamic nature of the ocean floor and the powerful forces at play beneath the surface.
Potential Impacts: Marine Life and Deep-Sea Exploration
While the eruption is unlikely to directly harm humans, it will undoubtedly impact the surrounding marine environment.Some marine life may even benefit from the new heat sources created by the eruption [[1]]. However, the long-term effects on the ecosystem are still being studied.
Challenges for Deep-Sea Exploration
The sinking of the ocean floor following the 2015 eruption presents challenges for deep-sea exploration. As we increasingly rely on robots to explore depths beyond human capabilities, changes to the seafloor topography can complicate navigation and data collection [[1]]. The Mariana Trench, the deepest part of the world’s oceans, is a prime example of an environment where robotic exploration is essential [[1]].
The scientific Perspective: Excitement, Not Alarm
Mike Poland, a scientist at the yellowstone Volcano Observatory, expresses excitement about the potential eruption.He emphasizes that Axial Seamount is “probably the best-monitored submarine volcano in the world” and that it “doesn’t really pose a hazard” [[1]]. Poland describes the expected eruption as similar to a Hawaiian lava flow, characterized by calm effusions of lava across the seafloor rather than explosive eruptions [[1]].
Comparing Axial Seamount to Yellowstone
While both Axial Seamount and Yellowstone are volcanically active, they represent vastly different types of volcanic systems. Yellowstone is a supervolcano with the potential for catastrophic eruptions, while Axial Seamount is a submarine volcano with relatively predictable and less hazardous eruptions. The monitoring techniques used at both locations, however, are crucial for understanding volcanic processes and mitigating potential risks.
the Broader Context: Underwater Volcanoes and Plate Tectonics
Axial Seamount is just one of many underwater volcanoes scattered across the globe. These volcanoes play a critical role in shaping the Earth’s crust and influencing ocean chemistry. They are often found along mid-ocean ridges, where tectonic plates are spreading apart and magma is rising to the surface.
The Juan de Fuca Ridge: A Hotspot of Volcanic Activity
Axial Seamount is located on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, a seismically active area where the Juan de Fuca plate is subducting under the north American plate. This subduction zone is responsible for the Cascade Range volcanoes, including Mount St. Helens and Mount Rainier. The interaction between these tectonic plates creates a complex geological environment with frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
FAQ: Understanding Axial Seamount
What is Axial Seamount?
Axial Seamount is a large, active underwater volcano located approximately 300 miles off the coast of Oregon in the Pacific Ocean [[1]].
Where is Axial Seamount located?
It is situated on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, a seismically active area in the Pacific Ocean, nearly 5,000 feet below the surface [[1]].
when did Axial Seamount last erupt?
The last eruption occurred in 2015 [[1]].
How do scientists monitor Axial Seamount?
Scientists use a variety of methods,including seismometers to detect earthquakes,pressure sensors to measure seafloor deformation,and underwater vehicles to observe volcanic activity directly [[1]].
Will the eruption of Axial Seamount affect humans?
Scientists believe that the eruption is unlikely to have any direct impact on humans [[1]].
What are the potential impacts on marine life?
While some marine life may benefit from the new heat sources, the long-term effects on the ecosystem are still being studied [[1]].
Could the eruption cause a tsunami?
Given the nature of past eruptions and the expected type of eruption, a large, destructive tsunami is considered unlikely. However, localized disturbances in the water are possible.
What does the future hold for Axial Seamount?
Scientists will continue to monitor Axial Seamount closely, using it as a natural laboratory to study volcanic processes and improve our understanding of underwater volcanism.
Pros and Cons of Monitoring Underwater Volcanoes
Pros:
- Improved Understanding of Volcanic Processes: Studying underwater volcanoes like Axial Seamount provides valuable insights into how volcanoes work, both on land and underwater.
- Early Warning Systems: Monitoring can help scientists develop early warning systems for potential eruptions, allowing for timely responses and mitigation efforts.
- Resource Management: Volcanic activity can create new mineral deposits and hydrothermal vents, which may have economic potential. Monitoring helps assess these resources sustainably.
- Advancements in Technology: The challenges of studying underwater volcanoes drive innovation in oceanographic technology, such as underwater robots and sensors.
Cons:
- High Costs: Monitoring underwater volcanoes requires significant financial investment in equipment, personnel, and research vessels.
- Technical Challenges: The deep ocean environment presents numerous technical challenges, including extreme pressure, corrosive seawater, and limited dialog capabilities.
- Limited accessibility: Access to underwater volcanoes is often difficult and time-consuming, limiting the frequency and scope of monitoring efforts.
- Unpredictability: Despite advances in monitoring technology, volcanic eruptions remain inherently unpredictable, making it difficult to provide accurate forecasts.
The Future of Underwater Volcanism Research
The study of underwater volcanoes is a rapidly evolving field, driven by technological advancements and a growing awareness of the importance of these geological features. future research will likely focus on developing more refined monitoring techniques, improving our understanding of the interactions between volcanoes and marine ecosystems, and assessing the potential hazards posed by underwater eruptions.
Advancements in Underwater Robotics
Underwater robots, also known as remotely operated vehicles (rovs) and autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs), are playing an increasingly important role in volcanism research. These robots can be equipped with a variety of sensors and instruments to collect data, take samples, and observe volcanic activity directly. Future advancements in robotics will likely lead to more capable and versatile underwater vehicles, allowing scientists to explore even the most remote and challenging volcanic environments.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence (AI) is also poised to revolutionize volcanism research. AI algorithms can be used to analyze large datasets from monitoring networks, identify patterns and anomalies, and improve the accuracy of eruption forecasts. AI can also be used to develop virtual reality simulations of volcanic eruptions, allowing scientists to study these events in a safe and controlled environment.
The potential eruption of Axial Seamount serves as a reminder of the dynamic forces shaping our planet. While the eruption itself may not pose a direct threat to humans, it offers a unique possibility for scientists to study underwater volcanism and improve our understanding of these interesting geological phenomena. As technology advances and our knowledge grows, we will be better equipped to monitor, predict, and mitigate the potential hazards posed by underwater volcanoes around the world.
Share this article with your friends!
Leave a comment below!
Interview: Decoding the impending Axial Seamount eruption with Dr.Evelyn Reed
Time.news: Dr. Reed, thanks for joining us. Axial Seamount,an underwater volcano off the Oregon coast,seems to be making headlines. Can you explain what’s happening?
Dr. Evelyn Reed: Certainly.Axial Seamount is indeed displaying increased activity, suggesting a potential eruption. It’s located about 300 miles off the coast of Oregon on the Juan de Fuca Ridge, a very active tectonic area [[1]]. Scientists have been monitoring it closely, especially as its last eruption in 2015. The current signals – increased earthquakes and seafloor deformation – are mirroring what we saw leading up to that event.
Time.news: So, an underwater volcanic eruption is imminent? What does that really meen?
Dr. Reed: “Imminent” in geological terms is relative. Some scientists believe an eruption could occur relatively soon, maybe even in the coming weeks or months. A more conservative estimate places it sometime later this year or early 2026 [[1]]. It’s significant to remember that predicting volcanic activity is inherently challenging. But, because Axial Seamount is so well-monitored, we have a good handle on what’s likely to happen.
Time.news: The article mentions the 2015 eruption. What did we learn from that event,and how does it inform our understanding today?
Dr. Reed: The 2015 eruption was a crucial case study. It triggered thousands of earthquakes and caused the ocean floor to sink by about eight feet [[1]]. This seafloor subsidence is a key indicator of magma movement. By monitoring such deformation, we gain valuable insights into the timing and intensity of potential eruptions. We can correlate patterns in seismic activity and deformation with magma chamber dynamics.
Time.news: Underwater volcanic eruptions frequently enough conjure images of tsunamis and devastation. Is there cause for alarm?
Dr. Reed: Fortunately, no. Experts indicate that the eruption is unlikely to directly impact humans [[1]]. The expected eruption is more akin to a calm Hawaiian lava flow, where lava effuses across the seafloor rather than exploding violently. A large, destructive tsunami is considered highly unlikely, tho localized disturbances in the water are possible.
Time.news: So,if it’s not a disaster,why is this significant? What are the real implications of an Axial Seamount eruption?
Dr. Reed: There are several key implications. Firstly, it provides an invaluable opportunity to study underwater volcanism in real-time. axial Seamount is the most active volcano on the Juan de Fuca Ridge,and its location makes it relatively accessible for intensive monitoring [[1]]. Secondly, eruptions inevitably impact marine life. While some organisms may benefit from the new heat and chemical sources, the long-term ecosystem effects are still being investigated [[1]]. Studying these changes is critical for understanding deep-sea ecology.changes to seafloor topography,like the sinking observed in 2015,present challenges for deep-sea exploration