The Future of Tuberculosis Diagnostics: A Deep Dive into rt-LAMP and Emerging Technologies
Table of Contents
- The Future of Tuberculosis Diagnostics: A Deep Dive into rt-LAMP and Emerging Technologies
- Revolutionizing TB Diagnostics with rt-LAMP
- Addressing Current TB Diagnostic Challenges
- Licensing and Validation: The Road Ahead for rt-LAMP
- Localized American Context: TB Diagnostics and Future Directions
- Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
- Expert Opinions: The Road to Broader Adoption
- Exploring Future Directions in TB Testing Technology
- Interactive Elements to Enhance Understanding
- FAQs: Your Questions Answered
- Conclusion
- Time.news Exclusive: A game-changing TB Diagnostic? Expert Weighs In on rt-LAMP
What if a simple, cost-effective test could revolutionize the way tuberculosis (TB) is diagnosed, saving countless lives in the process? The recent developments by researchers at the Sree Chitra Tirunal Institute for Medical Sciences and Technology (SCTIMST) are not just promising—they could reshape the entire landscape of TB detection.
Revolutionizing TB Diagnostics with rt-LAMP
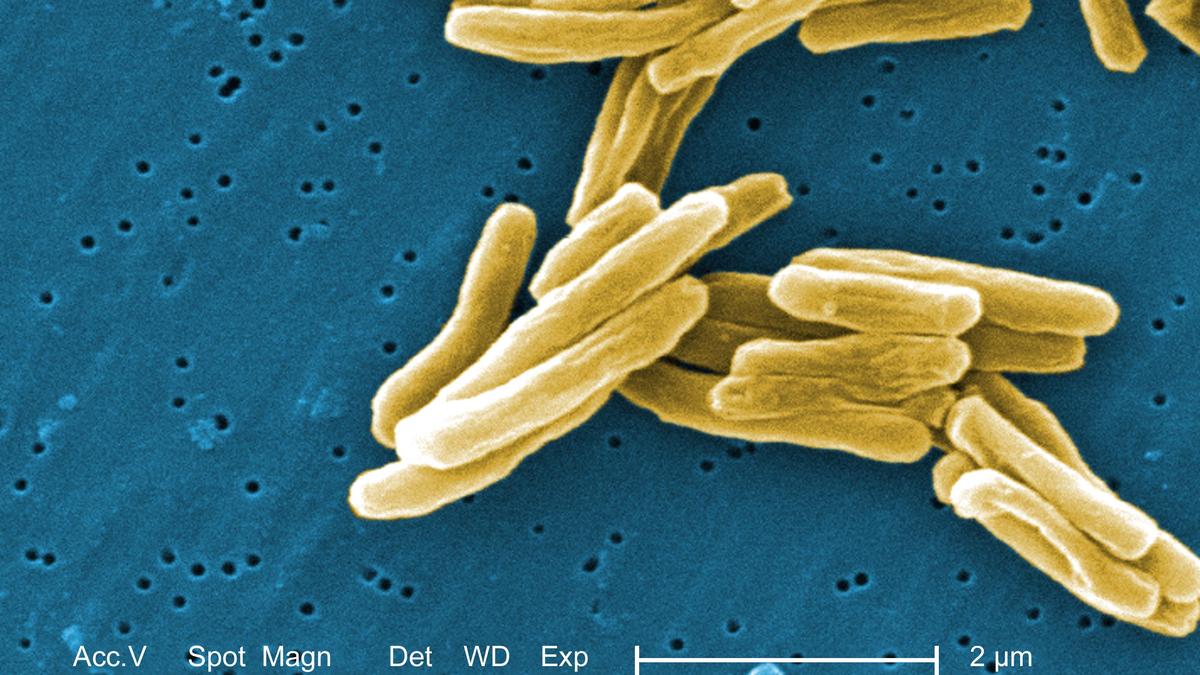
The rt-LAMP (real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification) assay is a game-changer in the battle against tuberculosis. Unlike traditional methods, which often take days to yield results, the rt-LAMP test can provide results in as little as 10-20 minutes, depending on the sample. Imagine a world where patients are diagnosed swiftly and accurately, minimizing the risk of transmission and enabling timely treatment.
Breaking Down the Science: How rt-LAMP Works
This revolutionary method enables the detection of TB DNA at extraordinarily low levels—just 10 copy numbers per microliter in a sample. Traditional RT-PCR tests require multiple temperature changes during processing, complicating the diagnostic process. In contrast, rt-LAMP operates at a single temperature, greatly simplifying logistics in low-resource settings and enabling high-throughput testing of up to 384 samples in one run.
Why rt-LAMP Outshines Other Testing Methods
The rt-LAMP assay’s design employs a unique approach with six primers compared to the two found in RT-PCR tests. This means that it has a higher amplification rate, leading to quicker and more specific results. With 89.36% sensitivity and 94.06% specificity against microbiological reference standards, the assay has demonstrated an edge over the widely used GeneXpert system. This could mean fewer false negatives and a more reliable detection pathway for clinicians.
Addressing Current TB Diagnostic Challenges
Despite advancements, TB diagnosis in India remains heavily reliant on sputum smear microscopy, with a staggering 79% of presumptive cases diagnosed this way as of 2023. With only 21% using molecular assays, it’s clear that traditional methods still dominate the landscape. The increase in molecular testing facilities from 5,090 in 2022 to 6,496 in 2023 is a step forward, yet it’s not enough.
The Need for Change: Understanding Global TB Statistics
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that TB is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide. In the United States, while it has been largely controlled since the early 2000s, health officials still maintain vigilance as new cases emerge annually. The potential for innovative diagnostic tests like the rt-LAMP could assist in curbing these numbers significantly.
Licensing and Validation: The Road Ahead for rt-LAMP
One of the most noteworthy elements of this new assay is its open platform system, which allows existing RT-PCR machines to be modified for TB testing. This adaptability could lead to widespread implementation in developing countries, where resources are sparse, but the need for efficient TB diagnostics is critical. Approval by the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO) and validation from the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) are crucial next steps.
Global Collaboration in Health Technology
The WHO Health Technology Access Pool’s interest in evaluating rt-LAMP highlights the growing recognition of this technology’s potential. Collaborations such as these could facilitate broader access to life-saving diagnostics in countries with high TB burdens.
Localized American Context: TB Diagnostics and Future Directions
In the United States, innovations like rt-LAMP could not only improve diagnostic speed but also affect public health responses to TB outbreaks. Current monitoring and response strategies hinge on timely and accurate diagnostics. Enhanced methodologies could allow public health agencies to mobilize resources more effectively during outbreaks.
The Intersection of Technology and Public Policy
Federal initiatives to combat TB include expanded funding for research on novel diagnostics. The continued focus on affordable health care solutions is critical, especially as the U.S. grapples with disparities in health care access. Integrating affordable technologies such as rt-LAMP into the diagnostic toolkit would represent a significant leap forward.
Challenges and Considerations for Implementation
While the prospects of rt-LAMP are compelling, there are significant challenges ahead. Training healthcare personnel to utilize new technology, while ensuring the accuracy and reliability of results, is paramount. Moreover, developing strategies to integrate this technology into existing health care frameworks will require concerted effort across various stakeholders, including government bodies, health organizations, and educational institutions.
Pros and Cons of rt-LAMP in TB Diagnostics
Pros:
- Rapid results that aid in timely treatment.
- High specificity and sensitivity reduce the likelihood of false negatives.
- Affordability and adaptability make it suitable for low-resource settings.
- Facilitates high-throughput testing capabilities.
Cons:
- Requires initial investment and training for health care providers.
- Possible need for continuous maintenance and calibration of equipment.
- Dependence on the availability of fluorescent dyes.
Expert Opinions: The Road to Broader Adoption
Dr. Anoopkumar Thekkuveettil, one of the leading researchers behind the rt-LAMP innovation, notes the importance of this technology: “It is all about increasing accessibility and doing it affordably.” As governments worldwide, including the U.S., consider how best to tackle TB, the emphasis on incorporating new technologies into routine practice cannot be overstated.
The Role of Education and Awareness
Public awareness campaigns and educational initiatives regarding the significance of early TB detection can enhance community engagement in health. Encouraging patients to seek testing and utilizing novel diagnostic methods could result in lower transmission rates and better health outcomes.
Exploring Future Directions in TB Testing Technology
As the rt-LAMP assay begins to find its place in the diagnostic landscape, researchers are exploring further innovations in TB detection. Blockchain technology, artificial intelligence (AI) for data analysis, and sensor technologies could optimize the efficacy of testing and treatment protocols. The interplay of these technologies may also offer real-time tracking of health trends, enhancing public health responses.
Innovations Beyond rt-LAMP
The scope of diagnostic tools is expanding beyond rt-LAMP. Technologies utilizing CRISPR for gene editing are also on the horizon. Researchers are investigating how these advanced methods can be adapted for TB testing, providing a future where diagnostics are cheaper, faster, and more accurate than ever before.
Interactive Elements to Enhance Understanding
Did You Know? Approximately 10 million people globally were diagnosed with TB in 2019 alone.
Expert Tips: Ensure that TB tests are included as part of routine health screenings, especially for individuals in high-risk categories.
Reader Poll: Would you prioritize rapid testing methods if they could significantly reduce TB transmission rates?
FAQs: Your Questions Answered
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the rt-LAMP test?
The rt-LAMP test is a molecular diagnostic assay that detects tuberculosis DNA with high sensitivity and specificity, providing results within 10-20 minutes.
How does rt-LAMP compare to traditional methods?
Unlike traditional smear microscopy, rt-LAMP offers faster results and higher specificity, significantly reducing the chances of false negatives.
Why is rapid TB testing important?
Rapid TB testing is crucial for early diagnosis, which enables timely treatment and reduces the risk of spreading the infection.
Conclusion
As tuberculosis continues to pose a significant public health challenge worldwide, innovative diagnostics like rt-LAMP stand out as beacons of hope. The intersection of accessible technology, education, and effective public health policies could ultimately redefine how TB is diagnosed and treated, ushering in a new era in global health.
Time.news Exclusive: A game-changing TB Diagnostic? Expert Weighs In on rt-LAMP
Keywords: Tuberculosis diagnostics, rt-LAMP, rapid TB test, TB testing, molecular diagnostics, global health, public health, TB treatment, GeneXpert
Time.news: Tuberculosis (TB) remains a major global health threat.A recent breakthrough promises to revolutionize how we diagnose this deadly disease: rt-LAMP, or real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification. To understand the potential impact of this technology, we spoke with Dr. Eleanor Vance,a leading expert in infectious disease diagnostics. Dr. Vance, welcome.
Dr. Vance: Thank you for having me.
Time.news: Dr. Vance, this article highlights rt-LAMP as a potential “game-changer” for TB diagnostics. What makes it so promising?
Dr. Vance: The promise of rt-LAMP lies in its speed, accessibility, and accuracy. Conventional TB testing methods, like sputum smear microscopy, can be slow and lack sensitivity. rt-LAMP, on the other hand, offers rapid results – frequently enough within 10-20 minutes. Critically, it boasts high sensitivity and specificity, comparable or even superior to the widely used GeneXpert system. This means fewer false negatives and more reliable diagnoses, allowing for quicker initiation of TB treatment and reduced transmission.
Time.news: The article mentions that only 21% of TB diagnoses in India rely on molecular assays, even though there’s been an increase in facilities. Does this point to a wider global issue of reliance on outdated methods?
Dr. Vance: Absolutely. Globally,access to advanced molecular diagnostics for TB remains limited,particularly in low-resource settings where the burden of disease is highest. Factors like cost, infrastructure requirements, and the need for trained personnel contribute to this disparity.The reliance on sputum smear microscopy, while sometimes necessary, unfortunately misses a important number of cases, hindering effective TB control efforts.
Time.news: rt-LAMP’s open platform is also discussed – the ability to adapt existing RT-PCR machines for TB testing. How significant is this in terms of potential scalability?
Dr. Vance: The open platform aspect is a huge advantage. one of the greatest roadblocks to widespread adoption of molecular diagnostic tests is the investment necessary in fully new equipment. The ability to adapt existing RT-PCR machines, commonly found even in resource-limited laboratories, lowers the barrier to entry substantially.This allows for a more rapid and cost-effective scale-up of TB molecular testing capabilities, making it accessible to a broader population.
Time.news: What are the key barriers to wider implementation of rt-LAMP, and what steps need to be taken to overcome them? This news article also mentions the need for training and maintenance, alongside equipment upkeep.
Dr. Vance: Several challenges exist. First,validating and approving rt-LAMP through regulatory bodies like the CDSCO and ICMR is crucial. Demonstrating its efficacy and reliability in diverse settings is essential for building confidence and securing widespread adoption. Then, healthcare personnel need proper training on how to perform and interpret the rt-LAMP test. Maintaining equipment and ensuring a reliable supply of reagents, like fluorescent dyes, are also critically important considerations. integrating rt-LAMP into existing healthcare systems requires careful planning and coordination between various stakeholders, including government agencies, NGOs, and healthcare providers. Pilot programs and exhibition projects can help identify and address potential challenges before large-scale implementation.
Time.news: The article touches on the role of global organizations like the WHO Health Technology Access Pool. How important are these collaborations for accelerating the adoption of new TB diagnostics like rt-LAMP?
Dr. Vance: Global collaborations are critically important. Organizations like WHO play a vital role in evaluating and recommending new technologies, developing guidelines for implementation, and facilitating technology transfer to countries with high TB burdens. Thier involvement can help ensure that rt-LAMP meets international quality standards and is accessible to those who need it most. Furthermore, collaborative efforts can mobilize resources, share best practices, and address challenges collectively.
Time.news: What advice would you offer to healthcare professionals and policymakers considering adopting rt-LAMP in their communities?
Dr. Vance: I’d advise them to carefully evaluate their existing TB diagnostic infrastructure and identify areas where rt-LAMP could offer the greatest benefit. Consider starting with pilot programs to assess its feasibility and impact in their specific context. Invest in training programs to ensure that healthcare personnel are proficient in performing and interpreting the test. Collaborate with other stakeholders to develop strategies for integrating rt-LAMP into existing healthcare systems. And advocate for policies that support the adoption of innovative TB diagnostics and ensure equitable access to quality healthcare.
Time.news: The article also mentions that new technologies like CRISPR, AI and blockchain might be used for TB diagnostics in the future. What are your thoughts?
Dr. Vance: It is exciting to see new technologies being used to fight this persistent health pandemic. CRISPR is very high potential for creating cheap, portable and rapid detection of TB.AI will only improve the speed and efficacy of testing and treatment, and blockchain technology could possibly improve tracking of health trends. With these tools, TB diagnostics can only get better. Though, as always, they must be implemented and used effectively in order for them to be helpful for the world at large.
Time.news: Any final thoughts for our readers?
Dr. Vance: Remember that early and accurate TB diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and preventing the spread of the disease. Be aware of the symptoms of TB and seek medical attention if you suspect you may be infected. Support efforts to improve access to TB diagnostics and treatment in your community and around the world.
Time.news: Dr.Vance, thank you for your insights. This has been a very informative discussion.
dr. Vance: My pleasure.