“`html
Tattooed tardigrades: A Glimpse into the Future of Bio-Integrated Technology
Table of Contents
- Tattooed tardigrades: A Glimpse into the Future of Bio-Integrated Technology
- The Unlikely Pioneers: Tardigrades and Microfabrication
- Beyond Tattoos: The Future of Bio-Integrated Devices
- Challenges and Opportunities
- FAQ: Your Questions Answered
- Pros and Cons of Bio-Integrated Technology
- The Future is Tattooed Tardigrades: Revolutionizing Bio-Integrated Tech? A Conversation with Dr. aris Thorne
Imagine a world where microscopic sensors are seamlessly integrated into living tissue, monitoring health, delivering targeted therapies, and even enhancing biological functions.Sounds like science fiction? Think again. Scientists are already taking the first steps, and it involves…tardigrades?
The Unlikely Pioneers: Tardigrades and Microfabrication
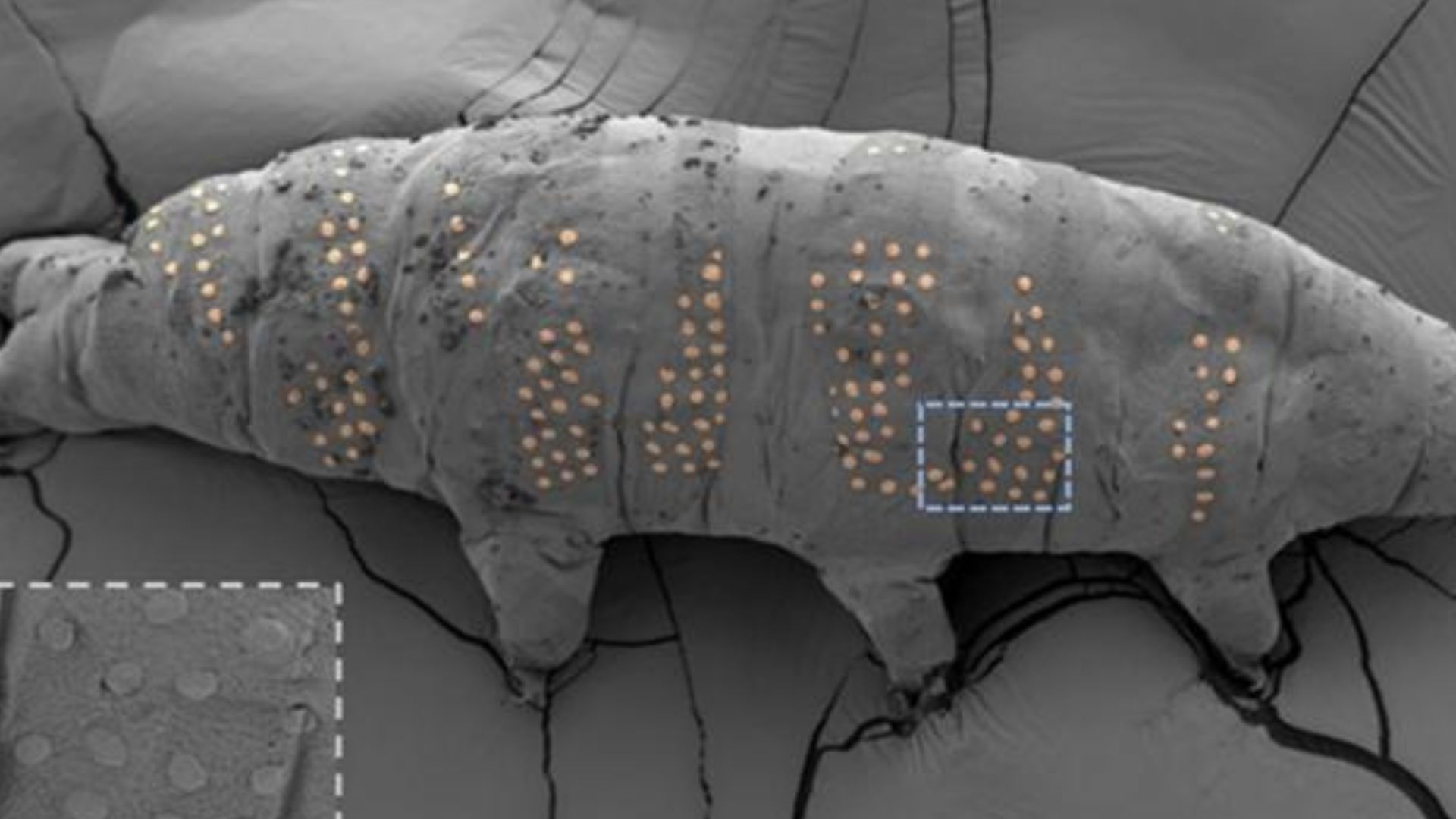
Tardigrades, those adorable, nearly indestructible “water bears,” are at the forefront of a revolution in microfabrication. Researchers have successfully “tattooed” these tiny creatures with micro-patterns, opening up a world of possibilities for bio-integrated technology [[1]], [[2]], [[3]]. But why tardigrades, and what does this mean for the future?
Why Tardigrades? The Perfect Test subjects
Tardigrades are renowned for their extreme resilience. They can withstand freezing temperatures, intense radiation, the vacuum of space, and pressures six times greater than those found in the deepest ocean trenches. this hardiness makes them ideal candidates for testing new microfabrication techniques. If a process works on a tardigrade, it’s likely to be compatible with other, more delicate biological systems.
The “Tattooing” Process: Ice lithography Explained
The “tattooing” isn’t about aesthetics. Researchers at Westlake University in China used a technique called ice lithography to create precise micro/nanoscale patterns on the tardigrades’ surfaces [[2]].This involves freezing the tardigrades, coating them with a protective layer of anisole, and then using an electron beam to draw patterns on the anisole. The exposed anisole transforms into a biocompatible material that adheres to the tardigrade’s surface, leaving behind the “tattoo” after the unreacted anisole is removed.
Ice Lithography: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Suspended Animation: Tardigrades are dried out to induce a state of suspended animation.
- Freezing: The microscopic organisms are frozen to -226 degrees Fahrenheit (-143 degrees Celsius).
- Protective layer: A layer of anisole is applied to protect the tardigrade during the process.
- Electron Beam Patterning: An electron beam draws intricate patterns on the anisole layer.
- biocompatible Material Formation: The exposed anisole transforms into a biocompatible material that sticks to the tardigrade’s surface.
- Tattoo Revelation: as the tardigrades warm up,the unreacted anisole vanishes,leaving behind the tiny “tattoos.”
Beyond Tattoos: The Future of Bio-Integrated Devices
While the “tattooing” of tardigrades might seem like a quirky scientific endeavor, it represents a significant leap forward in the development of bio-integrated devices. The ability to create precise micro/nanoscale patterns on living organisms opens up a vast array of potential applications.
Microbial Cyborgs: Enhancing Biological Functionality
One exciting possibility is the creation of “microbial cyborgs.” By integrating microelectronics and sensors directly onto microorganisms, scientists could enhance their natural abilities. Imagine bacteria equipped with sensors that can detect pollutants in the surroundings or deliver targeted drugs to specific locations in the body. This could revolutionize environmental monitoring, drug delivery, and even bioremediation.
Revolutionizing Biomedical Applications
The ability to print micro-electronics or sensors directly onto living tissue could also revolutionize biomedical applications. Imagine implantable sensors that continuously monitor vital signs, deliver medication on demand, or even stimulate nerve regeneration. This could lead to more effective treatments for a wide range of diseases and injuries, from diabetes and heart disease to spinal cord injuries and Alzheimer’s disease.
Potential Biomedical Applications: A Closer Look
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring: Implantable sensors could continuously monitor glucose levels in diabetic patients, eliminating the need for frequent finger pricks.
- Targeted Drug Delivery: Micro-devices could deliver drugs directly to cancer cells, minimizing side effects and improving treatment efficacy.
- Nerve Regeneration: electrical stimulation from implanted micro-devices could promote nerve regeneration after spinal cord injuries.
- Brain-Computer Interfaces: Micro-electronics could be used to create more complex brain-computer interfaces, allowing paralyzed individuals to control prosthetic limbs or communicate with the outside world.
The American Advantage: Innovation and Investment
The United States is well-positioned to lead the way in the development of bio-integrated technology. With its strong research universities, vibrant biotech industry, and robust venture capital ecosystem, America has all the ingredients necessary to translate these scientific breakthroughs into real-world applications. Companies like Medtronic, Abbott, and Boston Scientific are already investing heavily in microelectronics and sensor technology, paving the way for the next generation of bio-integrated devices.
The Role of DARPA and NIH
Government agencies like DARPA (Defence Advanced Research Projects Agency) and the NIH (National Institutes of Health) also play a crucial role in funding and supporting research in this area.DARPA’s focus on national security applications could drive innovation in areas like biosensors for detecting biological threats, while the NIH’s emphasis on improving human health could accelerate the development of new diagnostic and therapeutic tools.
Challenges and Opportunities
While the future of bio-integrated technology is bright, there are still significant challenges to overcome. One of the biggest hurdles is improving the survival rate of organisms undergoing microfabrication. In the tardigrade “tattooing” experiment, only 40% of the creatures survived the process [[1]], [[2]], [[3]]. researchers need to refine their techniques to minimize damage to living tissue.
Ethical Considerations: A Brave New World?
As with any new technology, there are also ethical considerations to address. As we begin to integrate technology more closely with living organisms, we need to carefully consider the potential risks and benefits. What are the long-term effects of implanting micro-devices in the human body? How do we ensure that these technologies are used responsibly and ethically? These are questions that society needs to grapple with as we move forward.
The Path Forward: collaboration and Innovation
The key to unlocking the full potential of bio-integrated technology lies in collaboration and innovation. Scientists,engineers,ethicists,and policymakers need to work together to develop safe,effective,and ethical applications of these groundbreaking technologies. By fostering a culture of innovation and investing in research and development, we can pave the way for a future where bio-integrated devices improve human health, protect the environment, and enhance our understanding of the natural world.
FAQ: Your Questions Answered
Hear are some frequently asked questions about tardigrade “tattooing” and the future of bio-integrated technology:
- What are tardigrades?
- Tardigrades, also known as water bears, are microscopic animals known for their extreme resilience.
- What is ice lithography?
- Ice lithography is a microfabrication technique that uses an electron beam to create patterns on a thin layer of ice coating living tissue.
- why are scientists “tattooing” tardigrades?
- The “tattooing” is a way to test and refine microfabrication techniques for creating bio-integrated devices.
- What are the potential applications of bio-integrated technology?
- Potential applications include microbial cyborgs, implantable sensors, targeted drug delivery, and nerve regeneration.
- What are the ethical considerations of bio-integrated technology?
- Ethical considerations include the long-term effects of implanting micro-devices in the human body and ensuring responsible and ethical use of these technologies.
Pros and Cons of Bio-Integrated Technology
Here’s a balanced look at the potential benefits and drawbacks of bio-integrated technology:
Pros:
- Improved Healthcare: More effective treatments for diseases and injuries.
- enhanced Environmental Monitoring: Real-time detection of pollutants and toxins.
- Increased Understanding of Biology: New insights into the workings of living systems.
- Potential for Human Enhancement: Improved cognitive and physical abilities.
Cons:
- ethical Concerns: Questions about privacy, autonomy, and the definition of “human.”
- Safety Risks: Potential for adverse reactions or long-term health effects.
- Accessibility Issues: Unequal access to these technologies could exacerbate existing social inequalities.
- Unintended Consequences: Unforeseen impacts on the environment and society.