“Every week the ISS presents a report on the effectiveness of vaccines and the data allow the information to be updated “: so said the Minister of Health, Roberto Speranza, last Wednesday announcing the green light to third dose even for people over i 40 years starting from December 1st. What does the latest report from the Higher Institute of Health say? “After the 6 months from the completion of the vaccination cycle, a sharp decrease vaccination efficacy in preventing diagnosis in correspondence of all age groups “. Regarding protection from the contagion, therefore, the effectiveness passes from 76% in the first 180 days compared to unvaccinated, al 50% after 6 months. In the case of severe disease, “The difference between vaccinated for over and less than six months is smaller”, specifies the ISS. However, a decrease in vaccination efficacy of about 10 percentage points: from 92% all’82%. It is the demonstration that, even if the risk of contracting Covid is halved compared to those who do not get vaccinated and the risk of ending up in hospital is even lower, without a strengthening of protection there is a risk of an increase in cases even among those vaccinated in the coming months.
The ISS first of all underlines the role of the Delta variant: “The vaccine efficacy in preventing any diagnosis symptomatic or asymptomatic Covid-19 in fully vaccinated people has decreased since 89%, during the epidemic phase with alpha variant prevalent, at 75% during the epidemic phase with the prevalent delta variant “. However, vaccination efficacy remains high, explains the Institute, “in preventing hospitalization (91%), hospitalization in intensive care (95%) or the death (91%) “. The other factor, however, is time, as the data show. Although the ISS highlights how the vaccination efficacy after 6 months can be in this moment underestimated. The reason? “The vaccination campaign initially involved the population most at risk (health workers, residents of the RSA, people with more than 80 years old and people extremely vulnerable) and only later was it opened to the rest of the population. It can therefore be assumed – the report reads – that currently the subjects who are vaccinated by over six months they are individuals at risk of infection / hospitalization / death more respect to the rest of the vaccinated population “.
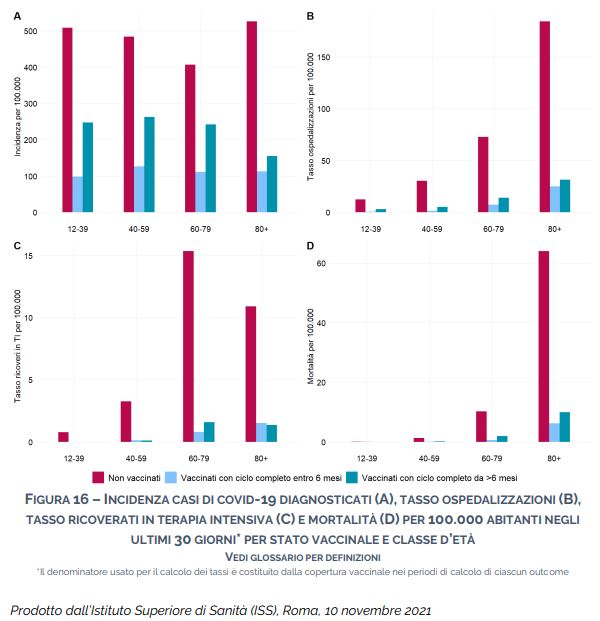
The decline in the effectiveness of vaccines, however, does not question the role that the vaccination campaign has had in slowing down infections and above all mitigating the pressure on the hospital (see figure above). By calculating the hospitalization rate for i not vaccinated (184.1 hospitalizations per 100,000), in fact, it is evident that this is approximately seven times higher compared to vaccinated with a full course for less than six months (25.0 hospitalizations per 100,000) e six times higher compared to vaccinated with a full course for over six months (31.5 hospitalizations per 100,000). Analyzing the number of hospitalizations in intensive care and gods deaths in the over 80s, it is observed that the rate of ICU admissions for unvaccinated people (10.9 ICU admissions per 100,000) is about seven times higher than that of vaccinated with a full course less than six months old (1.5 admissions to intensive care per 100,000) and for over six months (1.4 admissions to intensive care per 100,000) while, in the period from 17 September to 17 October, the death rate in the unvaccinated (64.1 per 100,000) is approximately ten times higher compared to vaccinated with a full course within six months (6.2 per 100,000) e six times higher compared to vaccinated with a full course for over six months (9.9 per 100,000).
Even looking at the new positives, he analyzes the ISS, “in last 30 days in Italy there is one higher incidence of cases diagnosed in people non vaccinate“. In general, the weekly incidence at the national level reaches 62 almost per 100 thousand inhabitants compared to 51 cases in the previous week. Up from the week beforeAverage Rt calculated on symptomatic cases equal to 1,21, stably above the epidemic threshold. The incidence increases in all age groups, but “in particular in the population 0-19 years characterized by a greater variation in the incidence at 14 days “. A slight increase the median age of the subjects who have contracted the infection in the last 14 days (43 years old compared to 42 years of the previous week).
